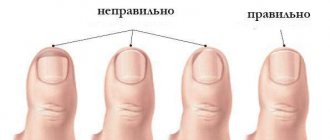
The main purpose of the stratum corneum on the fingertips is to protect the nerve endings located on the phalanges. The formation of nail plates occurs from keratinized cells. That is, there are no nerve fibers directly in the stratum corneum. When visiting a doctor, some patients are interested in why their fingernails hurt. In fact, discomfort occurs directly under or near the plates. Below is information about why fingernails hurt and how to quickly get rid of unpleasant symptoms.
Various types of injuries
If discomfort occurs in the area of only one plate, for example on the thumb or little finger, the most likely cause is a bruise.
It is necessary to carefully examine the condition of the stratum corneum. If there is even a slight hemorrhage underneath, the cause is definitely trauma. Regarding why there is pain on the hands under the nails in this case. When an injury occurs that is not accompanied by a violation of the integrity of the skin and stratum corneum, the capillaries located directly under the plate or next to it rupture. The natural result is the outpouring of liquid connective tissue.
Most often, you will notice dots, spots or stripes of dark burgundy or black under the nail. As the bruise resolves, it begins to take on a bluish tint.
After suffering a serious injury, it is recommended to consult a doctor. Minor injuries do not require treatment and go away on their own within a few days.
The nail hurts when pressed
Discomfort is not always felt in a calm state; pain often appears when pressing on the tip of the finger. Then the girl herself can recognize the reason for its appearance, since there are several factors that can affect this.
There are four main reasons for discomfort when pressing:
- Insertion of a splinter under the nail bed. It is associated with neglecting to wear protective gloves when processing wood and metal.
- The initial form of ingrowth on the legs. When the nail rests on the side cushion and gradually begins to damage it, pain appears at first only when pressed.
- Bruise. After mechanical damage to the nail, a bruise or hematoma forms.
- Exposure to chemicals. When aggressive components accumulate in the matrix, they gradually lead to unpleasant sensations.
You need to act as in the previous case - consult a doctor so that he can prescribe you a competent treatment regimen.
Felon
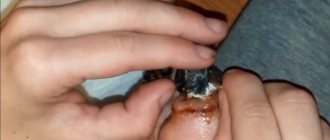
This term refers to acute inflammation of a purulent nature. The tissues of the finger from the nail side are involved in the pathological process.
The causative agent of felon is most often staphylococcus. Less commonly, the following pathogens are identified in patients: Proteus, Streptococcus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The infectious agent enters the body through minor injuries to the skin. Since the wounds are very small, most people do not treat them, which triggers the active life of the pathogen.
After some time, purulent exudate begins to form. The pathological fluid cannot come out; it spreads along the bridges of the subcutaneous fat layer. Over time, muscle tissue, ligaments, joints and tendons are damaged. This is why the fingers and toes under the nails hurt.
Clinical manifestations of the disease:
- A purulent mass that can be seen directly under the plate.
- Pronounced painful sensations of a pulsating nature.
- Swelling and redness of the fingertip.
As healing occurs, the stratum corneum peels off. The intensity of the pain decreases, and the pus resolves.
In practice, perilongated panaritium is often diagnosed. In this case, the skin ridge near the plate is involved in the pathological process. Why do fingernails hurt in this case? The infectious agent also penetrates the body, but through deeper damage.
Symptoms in this case develop after 5-6 days. Clinical manifestations of periungual felon:
- Strong pain.
- Redness and swelling of the skin fold. The tissues are stretched and as if they are about to burst.
- An accumulation of pus may be found under the skin.
- With deep damage, the pathological exudate rushes deep into the tissues, resulting in a loss of connection between the stratum corneum and the nail bed.
Treatment of panaritium is most often conservative. For deep lesions, surgical intervention is indicated, during which the doctor opens the abscess and removes the exudate. Sometimes the inflammation spreads to the bones. In this case, it is not always possible to save the finger.
Panaritium disease
This disease comes from the Latin word, translated as naileater. Felon is truly a nail eater, since the nail can be lost as a result of inflammation and suppuration.
This disease occurs when staphylococci or streptococci, as a result of some traumatic effect, penetrate the skin in the periungual area.
Moreover, the injury does not have to be large and serious. Sometimes a small scratch is enough. Women who get manicures are especially at risk. It is precisely because of the frequent traumatic effects in this area that felon develops on the side of the fingernail or in the center of the finger at the border of the skin and nail.
The peculiarity of this disease is the impossibility of spreading the inflammatory and purulent process throughout the skin of the entire hand. The specific structure of the hand and fingers does not allow the purulent process to spread along the plane. It is directed deeper along the connective tissue cords, as a result of which deep fibers, tendons, joints and even bones are affected. For this reason, the finger on the hand near the nail hurts especially severely. In addition, it swells and darkens. The pain is not only acute, but also throbbing.
The accumulation of pus in one place under the nail compresses the blood vessels, which leads to poor circulation. This, in turn, contributes to the development of tissue necrosis.
Typically, a person suffering from severe pain begins to take measures on his own or consults a doctor. However, if there are not enough of them, then suppuration will spread through the tendons, bones, and joints. Sometimes such processes end in the loss of a finger.
But this is not the worst thing. In some cases, the disease affects the entire finger, resulting in pandactylitis. This is already purulent tissue damage right down to the bone. If treatment is delayed, it usually ends in amputation of the finger.
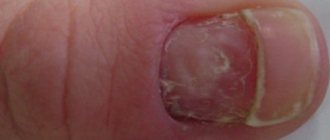
Onychomycosis
This is a pathology of an infectious nature, the causative agent of which is a fungus. As a result of the active life of the pathogen, one nail or several are affected.
The infection penetrates the stratum corneum, where it begins to form tunnels. As a result, the fingernails hurt when pressed.
Why does the pathological process develop:
- Visiting public places. A striking example are baths, saunas and gyms.
- Using the same household items. Very often, the pathogen is transmitted from one family member to another through towels, gloves, and washcloths.
Not in all cases, a pathological process develops during infection. The provoking factors are the following diseases and conditions:
- Various types of injuries.
- Immunodeficiency.
- Diabetes.
- Ignoring the need to observe hygiene rules.
Clinical manifestations of onychomycosis:
- Painful sensations under or near the nails.
- Change in color of the horny plate.
- Thickening of the nail.
- Plate deformation.
If signs of fungal infection occur, you should consult a dermatologist. The specialist will conduct diagnostic measures, tell you why your fingernails hurt and how to treat the disease.
Mechanical damage to toenails
Damage often occurs for reasons beyond our control. Such damage can be divided into 2 types:
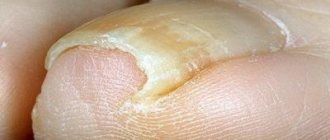
- Various injuries. Nails are most susceptible to them, since with any external physical impact on the fingers, they take the main load. Thus, damage or tearing of the nail plate, a pinched finger and a number of other injuries can cause long-term pain in the toenails. If the damage is particularly severe, the nail may gradually darken and eventually die off completely. This occurs if the bruise occupies more than 1/3 of the nail. A complete replacement of the plate takes place within 2-4 months. Color restoration occurs gradually, from darker to lighter tones.
- Onychocryptosis (a case where the nail plate grows firmly into the nail fold). Most often, this phenomenon affects the nails of the thumbs. This disease is a very common and extremely unpleasant illness. The main signs by which an ingrown toenail can be identified is the appearance of pain in the nail, accompanied by bleeding and inflammation of the soft tissues (the pain intensifies when wearing tight shoes and walking) and purulent discharge from the affected tissue. This situation may be the reason why the nails on the big toes hurt. Onychocryptosis is especially dangerous for patients with diabetes, as well as those suffering from vascular disorders, and, consequently, congestion in the lower extremities. In such cases, an ingrown toenail can trigger the development of gangrene. Ingrown toenails can be caused by:
- Incorrectly performed pedicure;
- Wearing tight shoes;
- fungus;
- Congenital predisposition;
- Orthopedic foot pathology.
Polyosteoarthrosis
This term refers to a chronic disease in which joints and bone tissue are damaged.
Regarding why the nail on the finger hurts in this case. Under the influence of any provoking factors, curvature and destruction of the joint and bone occur. Moreover, each patient complains of severe pain, which makes it almost impossible to bend the finger. When you press on the nail, discomfort also occurs.
The main reasons for the development of the disease:
- Natural processes of aging of the body.
- A lifestyle that does not involve physical activity.
- Various types of injuries to one or more fingers.
When trying to bend the phalanx, a crunching sound is heard. In some cases, the joint becomes so deformed that it becomes impossible to move the finger.
Treatment of the disease requires an integrated approach. It is completely impossible to get rid of the disease. The main goal of therapy is to stop the progression of the pathology and achieve a period of stable remission. If conservative methods are ineffective, the doctor evaluates the feasibility of surgical intervention.
Joints, nerves and blood vessels
Why do the fingers under the nails hurt, and not the plates themselves? Nails cannot hurt because they have no nerve endings. Otherwise it would be impossible to trim them. Pain always occurs in the tissue area with which the nails grow together. The blood vessels that supply the nails with everything they need are also located.
If the fingertips themselves hurt, and not the tissues located directly under the nails and next to them, this means that the person develops the following pathologies:
- Inflammation in the joints. In this case, pain is accompanied by swelling, redness and impaired ability to move freely. Rheumatoid arthritis usually affects the fingers. It is concentrated in several small joints of the hand. As a rule, the lesions are symmetrical. For example, only the index or middle fingers of both hands become ill. The appearance of such signs of rheumatoid arthritis is a signal to action. If this disease is not treated, the joints can be greatly transformed, and the hands will take on an irregular and, of course, ugly shape.
- Raynaud's syndrome. Otherwise it is called angiospastic peripheral crises. Signs of this disease manifest themselves in changes in skin color (blueness or pallor), coldness, small tingling sensations, numbness in the fingers or in the entire hand. Raynaud's syndrome is characterized by attacks that occur several times a day and last a certain number of minutes.
- Vascular diseases of the hands. More often they are sclerotic in nature. Vascular pathologies are manifested not only by pain in the fingertips and along their entire length, but also by periodic cramps, numbness, and rapid fatigue of the entire hand. The brushes are particularly pale. Usually they are not only cold to the touch - a person’s hands actually get cold all the time. The hair on the limbs begins to fall out, and the nails, on the contrary, thicken. As the pathology develops, the lumen in the vessels decreases, and the blood supply to the hands deteriorates. As a result, pain in the hands and, especially, fingers becomes constant. At the same time, the hands often and quickly get tired, and the pulse on the wrist is weak.
- Vibration disease. People who work with hand tools for a long time, which are a source of constant vibration, over time begin to feel mild pain, tingling, and numbness in their fingers. If a person does not change his lifestyle, then the symptoms of vibration disease intensify and become permanent. Gradually, from a local nuisance, this pathology becomes a problem for the whole organism. Signs of damage to the vascular system and, above all, vegetative-vascular dystonia and asthenia appear.
- Ulnar nerve neuropathy. This disease manifests itself as pain and paresthesia in the two outer fingers of the hand - the ring and little fingers. This is usually associated with injury to the elbow or wrist joint. Over time, hand movements may become difficult, the muscles atrophy, and the shape of the hand changes, taking on a “clawed” appearance.
- Damage to the cervical spine. As a rule, this affects the condition of the entire hand. Numbness appears and the pain threshold decreases. The fingers get the most sensations and troubles. Pain and numbness may occur in all fingers, or only in the ring and little fingers. If the cervical spine is affected by osteochondrosis, then this will certainly affect the hands. A person feels numbness, tingling, chilliness, decreased mobility, and rapid fatigue of the entire hand.
- Pain in the fingers always occurs when a hand injury occurs. A dislocation in the area of the elbow, hand, or fingers themselves, even with quick and correct reduction, will certainly affect the person’s condition. Your fingers will not only hurt and swell, they will even refuse to work for a while. When a ligament is sprained, the pain is concentrated mainly in the place where it was damaged. So in this case, the fingertip can only hurt when the ligaments are sprained in this particular part of the hand or in a nearby aponeurosis.
- Polycythemia. This pathology, which occurs when the number of red blood cells increases, gives rise to sensations of periodic pain in the fingertips, numbness and itching. All this is accompanied by weakness, headache and insomnia.
Thus, there are many reasons for pain in the fingers. The main thing in this case is to quickly and competently make a diagnosis and start treatment on time.
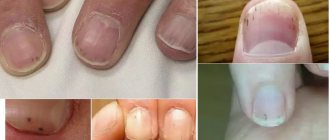
Almost every one of us at least once in our lives has encountered unpleasant pain localized in the area of the nail plates. Moreover, nails can periodically hurt not only in men who are not inclined to pay attention to proper hygienic care of the nail plates on the hands and feet. Many women who like to care for their nails at home are familiar with this problem and use professional manicure and pedicure tools. If your fingernails or toenails hurt, then first of all you need to find out the cause of the unpleasant symptoms, and then choose the appropriate treatment for the disease.
Healthy nails should have a pinkish tint, natural shine, and a smooth surface without compaction. If your nail plates become brittle, begin to peel, or other signs of deformation appear, be sure to visit a doctor so that a specialist can prescribe a comprehensive examination. As a rule, nails hurt after mechanical damage, as a result of fungal infection, as well as with the development of some infectious and non-infectious diseases of a non-fungal nature.
♦ MECHANICAL DAMAGE
Ingrown toenail (Onychocryptosis).
Pain appears after the nail plate grows into the side fold.
Onychocryptosis can develop on both the toes and fingers. But most often, an ingrown toenail is found on the big toe, causing acute pain, bleeding and inflammation of the soft tissues with purulent discharge. Reasons:
constant wearing of tight or narrowed shoes, incorrectly performed pedicure and cutting of nails “to the meat”, orthopedic pathology of the feet, hereditary predisposition.
Treatment:
soda baths, chamomile baths with castor oil, mechanical thinning of the entire plate with a file (to a thickness of approximately 0.1-0.2 mm), correction staples with cutting the plate on the sides, Lugol treatment. At stages 3-4 of onychocryptosis, treatment by a specialist in a clinic is indicated (radio wave treatment, laser removal).
Injuries.
Pinching the upper phalanx of the finger, tearing or damaging the nail plate with a heavy object can cause darkening of the nail. The bruise spreads under the nail, the structure of the plate is damaged and its complete replacement occurs within several months. Usually, after an injury, the nails hurt for several days, then the dark color of the plate gradually replaces it with lighter tones.
♦ NAIL DAMAGE BY FUNGUS
Onychomycosis.
Dermatophyte fungi affect the fingernails and toenails. Pressure on the nail plate is accompanied by unpleasant pain. With hypertrophic onychomycosis, the color of the nail changes, and the plate itself thickens. With atrophic onychomycosis, the affected plate is separated from the bed. Normotrophic onychomycosis causes discoloration and the appearance of stripes on the nails. Treatment:
drugs (Itraconazole, Griseofulvin, Fluconazole, Ketoconazole Terbinafine), ointments (Daktarin, Mycozon, Bifasam, Bifonazole, Bifosin, Mycospor, Exoderil, Atifin, Binafin, Lamisil, Myconorm).
The treatment course is prescribed by the doctor. Rubromycosis.
The red trichophyton fungus affects the nails and makes them brittle. Nails and side ridges hurt when pressed. The plates gradually become thinner or, on the contrary, thicken. Treatment:
ointments of Whitefield, Arievich; drying ointments Pimafucin, Mikozolon, Exoderil, Tolmitsen, Nizoral, Lamikon after treatment with a 2% iodine solution; fungicidal-keratolytic varnishes.
Candidiasis.
The fungus is usually introduced during a pedicure with a poorly disinfected instrument through wounds and cuts. Candidiasis causes pain, inflammation and swelling in the soft tissue of the nail. Treatment:
antimycotic drugs - Fluconazole, Ketoconazole, Itraconazole;
ointments - Pimafucin, Mycoseptin, Clotrimazole, Ketoral. Ringworm (microsporia).
The nail plate thickens and becomes colorless as the infection moves deeper into the plate. Ringworm can affect both the toes and fingers. The disease gradually progresses and the nails hurt more and more. Treatment:
antifungal drugs and ointments (Termikon, Clotrimazole, Terbizil). If microsporia is complicated by a secondary infection, Triderm ointment is used.
Athlete's foot.
The fungal infection affects the nail plate and then spreads to the skin around the nail. The color of the nail becomes yellow or brownish, and the plate itself becomes deformed and begins to crumble. The periungual skin becomes inflamed and red. Treatment:
removal of the nail plate followed by treatment of the bed with fungicidal agents (Krichevsky liquid, Nitrofungin) and aniline dyes (Fukortsin).
♦ INFECTIOUS DISEASES
Felon.
Pyogenic bacteria penetrate the soft tissue around the nail through small wounds and cuts.
The first symptom of panaritium is acute pain spreading to the top of the finger when pressing on the nail. Gradually, the color of the ridges around the nail becomes dark red, and the plate becomes deformed. Panaritium affects both fingers and toes. Treatment:
at home can be treated only at the initial stage of the disease.
Dimethyl sulfoxide is diluted 1:4 with boiled water, a small piece of gauze is soaked in this solution and a compress is applied to the finger. If severe pain bothers you, the doctor opens the abscess. Onychorrhexis and onychoschisis.
Infection of the nail grooves with pathogenic bacteria can cause destruction of the nail structure. The plate begins to split in the transverse direction (onychoschisis) or longitudinally (onychorrhexis). Gradually the plate changes color and peels off. Treatment:
preparations with a local disinfecting effect (chrysarobin solution in chloroform, synthomycin emulsion, tinol alcohol solution, heliomycin ointment).
♦ NON-FUNGAL DISEASES
Onychomadesis.
Disruption of the normal functioning of the root (matrix). As a result of the pathology, the nail plate begins to move away from the bed, starting from the base of the nail. The nail hurts even when you press lightly on the plate. Treatment:
finger massage to normalize the functioning of the matrix, vitamin therapy, chondroprotectors (glucosamine, chondroitin sulfate).
Onyhauxis.
An infection gets into the soft tissues and the inflammatory process begins in the bed and nail folds. The nail plate increases in size and becomes thicker. The nail hurts even when you press on the pad of your finger. Treatment:
drugs are prescribed that help strengthen the vascular wall (Detralex, Venodiol, Phlebodia).
Onycholysis.
The nail plate begins to move away from the free edge and side ridges. The soft periungual tissues become inflamed. Treatment:
restorative therapy: iron supplements, calcium, vitamins A and B, gelatin;
syntomycin emulsion, heliomycin ointment; solution of chrysarobin in chloroform. Onychogryphosis.
The color of the nail plate changes to dirty brown, and the plate itself becomes deformed, thickens, elongates and becomes claw-like. Onychogryphosis can develop on both the toes and hands. Treatment:
nail removal using onycholysin; the use of ointments that contain gelatin, ichthyol, retinol, vitamin A.
Scleronychia.
Malfunction of the matrix causes hypertrophy of the nail, its thinning and separation from the bed. Treatment:
complex therapy (Trental, Doxium, Ascorutin to improve blood microcirculation in the fingers; keratoplasty drugs).
Micronychia.
Nails grow poorly and do not completely cover the bed. When pressing on the stock with a short plate, pain is felt. Treatment:
general strengthening therapy (vitamins A and E, Aevit, retinol palmitate).
♦ VIDEO MATERIALS
Unbalanced diet
Many people do not adhere to the principles of a healthy lifestyle. Meanwhile, its basis is proper nutrition. Regular consumption of junk food negatively affects the functioning of the body's defense system. The consequence of this condition is the deterioration of the stratum corneum.
It’s worth figuring out why your hand hurts near or under the nail. Due to the deficiency of vital components, the plate becomes thinner and breaks easily. This in all cases leads to painful sensations. Sometimes they only appear when you press on the nail.
In order to get rid of discomfort, it is necessary to make adjustments to the diet. Additionally, it is recommended to make hand baths with sea salt.
Cosmetics and procedures
Some women experience discomfort after removing nail polish. In this case, the tips of the fingernails most often hurt. Why is this happening? It is important to know that any varnish and its remover penetrate the stratum corneum and contribute to changes in its structure. Most often, painful sensations occur at the tips of the nails immediately after pigment removal.
Discomfort may also occur after removing the materials intended for plate extension. Its appearance is due to a long period of lack of access to light and air to the nails.
First aid
In most cases, pain in the fingertips significantly impairs the quality of life. To get rid of them for a while, you can make baths with chamomile, sea salt or baking soda. It is recommended to carry out the procedure several times a day.
In case of fungal infection, ammonia can be used. A tablespoon of liquid must be added to a glass of water. Moisten a piece of gauze in the resulting product and apply it to the affected area for half an hour.
Doctors' recommendations
To prevent painful sensations under or near your nails, you must follow these rules:
- Treat all identified diseases, including those of a chronic nature, in a timely manner.
- Use protective gloves when handling household chemicals.
- Carry out cosmetic procedures in strict accordance with standards. Don't abuse them.
- Even with a slight violation of the integrity of the skin, treat the lesions with antiseptics.
- Strengthen the body's defenses.
- Take vitamin complexes.
- Follow the principles of proper nutrition.
In addition, doctors advise getting rid of bad habits.
Why do fingernails hurt: reasons
It is important to clarify that the nail plate cannot hurt; it has no nerve endings. Therefore, only the nail bed, where there are nerve endings, can hurt.
As mentioned earlier, the health of nails depends on the general health of a person; if there are inflammatory processes or chronic diseases in the body, this will certainly affect the health of the nails. Therefore, if you have pain in your nails, you should be examined by a doctor and find out the cause of the pain in order to prescribe treatment.
The main causes of pain in nails
Hormonal background
Hormonal disruptions and surges can lead to pain in the nails (pregnancy, adolescence, menstruation).
Lack of vitamins, macro and microelements. A lack of essential vitamins, micro and macroelements leads to the body sending signals about a lack of nutrition to a person through pain in the nails.
Unbalanced diet
An unbalanced diet is associated with a fast pace of life, we eat incorrectly, when it happens and what happens, this especially often happens during working hours. Also, in their quest for an ideal body, girls go on diets and eat poorly. This is a big mistake! The fact is that the body needs balance in everything, including nutrition.
Lack of calcium in the body
The nail is made of keratin, and keratin is made of calcium. Therefore, calcium is the basis for healthy nails. Calcium strengthens nails, protects them from brittleness and nourishes the entire plate. If there is a lack of calcium in the body, the nails may hurt.
Intoxication of the nail plate on the hands
Nails can hurt from using low-quality cosmetics. The problem is that “bad” cosmetics contain prohibited and toxic substances. Toxic substances fall with the varnish onto the surface, after which they penetrate through the plate onto the nail bed. At the nail bed, toxic substances come into contact with the nerve endings of the fingers, causing the nails to hurt.
Nail polish remover
The nail plate is made up of water, but nail polish remover contains acetone, which dries and draws out water from it. Nails may hurt from dehydration and dryness, and the plate may crack and peel from exposure to acetone.
Manicure
In a manicure salon, your nails may be injured if the procedure is performed unprofessionally. The reason is that excessive filing of the nail plate or excessive pressure of the scapula (pusher) on the nail plate can cause injury to the nails. Such injuries cause pain. Choose proven and certified manicurists.
Exposure to chemicals
The cause of nail pain can be household chemicals or professional activities with chemicals. Chemicals corrode the protective layer of nails and can cause pain.