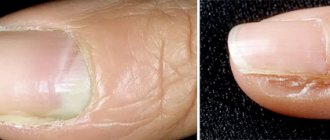
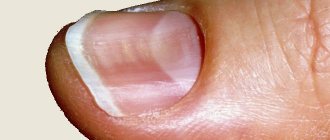
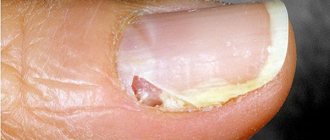
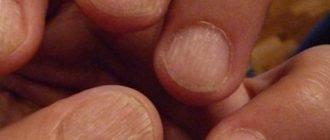
Onycholysis - causes
Establishing the correct cause of onycholysis will help you significantly reduce the treatment time and avoid recurrence of the disease. The causes can be both infectious and non-infectious.
Infectious causes
- Infection with a fungus that causes diseases such as candidiasis, epidermophytosis, rubrophytosis;
- Inflammation caused by pyrogenic bacteria - streptococci and staphylococci;
Non-infectious causes of appearance
- due to injury or compression of the nail;
- with vitamin deficiency;
- due to chronic diseases of the nervous, endocrine, digestive and cardiovascular
- vascular systems;
- for dermatological pathologies - allergic or atopic dermatitis, psoriasis,
- eczema;
- when taking antibiotics such as tetracycline and fluoroquinolones;
- in case of using low-quality varnishes;
- due to neurotic disorders (onychotillomania and onychophagia);
- upon contact with household chemicals and other aggressive substances;
Onycholysis, or nail detachment. Causes and treatment of onycholysis
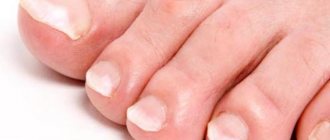
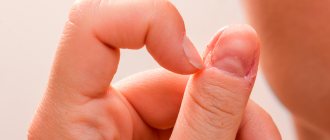
Onycholysis is the separation of the nail plate from the soft tissues of the phalanx of the finger on which the plate lies.
Despite the seeming pettiness of the problem, identifying the reasons for the detachment of the nail from the nail bed and proper treatment are just as relevant as for more complex dermatological problems. In the presence of onycholysis, a systematic approach is important. Despite the fact that the damage to the nail plate is often even less than one square centimeter, drug prescriptions can be systemic in nature; local treatment alone is not enough.
Before prescribing effective drugs for the treatment of onycholysis, it is necessary to determine whether the pathology is related to other diseases. If there is one, a local effect on the diseased nail plate will not have the desired effect - the provoking disease needs to be expelled.
Diseases that may cause nail plate detachment:
- pathology of the gastrointestinal tract;
- disorders of the cardiovascular system;
- pathology of the nervous system (central and peripheral);
- endocrine diseases;
- dermatovenerological diseases (eczema of various etiologies, psoriatic lesions, some dermatitis and dermatoses).
Therefore, the answer to the question of which doctor treats onycholysis will logically include a list of all the specialists who are involved in the relief of these pathologies.
Symptoms
Treatment of onycholysis should begin when the first symptoms appear. Detachment of the nail begins from the free edge of the nail plate, gradually spreading over the entire surface.
Onycholysis is divided into partial and complete. In case of partial, the area of detachment occupies no more than half of the nail plate. The peeled part may have the shape of a strip running along the free edge, a trapezoid, or a crescent. Less common is complete onycholysis, in which the entire nail plate is separated.
The appearance of the nail depends on the cause of onycholysis.
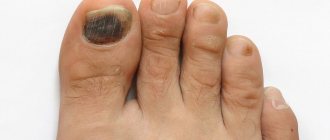
If the disease develops as a result of non-infectious factors, the nail plate remains smooth and even, and the color changes to whitish-gray. In case of injury, a hematoma may form under the nail, it may become deformed and turn black. Psoriasis provokes thickening, brittleness of nails, clouding and the appearance of pinpoint depressions on them.
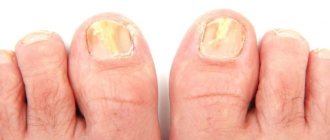
Infectious causes of onycholysis lead to significant changes in the nail. The plate thickens, grooves appear on it, acquires a yellow, brown or blue color, and without treatment it may become complicated by an inflammatory process, in which redness of the cushion, swelling, and suppuration occur.
In case of systemic and infectious pathologies, nail detachment may be accompanied by other symptoms:
- Psoriasis – the appearance of itchy red plaques on the head, skin folds, arms, legs;
- Eczema - the appearance on the body of a symmetrically located papular red rash;
- Vitamin deficiency - possible skin problems, hair loss, nails become brittle;
- Mycosis of the feet - thickening, peeling and dry skin of the feet.
The main causes of onycholysis
There are many reasons for such a common problem as onycholysis or nail separation. One of the most common is mechanical damage to the nail, which can occur due to a blow, cut, burn, rough tearing of the nail or other trauma. As a result, the structure of the nail is damaged and its growth is disrupted. In addition, dirt, dust and bacteria can enter the affected areas, which contribute to the development of infectious diseases. External factors can also include the influence of aggressive substances and allergens. A similar problem may arise for people who work in manufacturing or construction.
Another common cause of this disease is the presence of fungus on the nails. Fungus is an infectious lesion of the nail that occurs due to the entry and proliferation of bacteria. If not treated in a timely manner, it can affect the structure and growth of the nail, as well as cause the development of more serious diseases. Diseases that can influence the development of onycholysis are: eczema, dysbacteriosis, psoriasis, vascular pathologies, metabolic disorders, lack of vitamins. As a rule, treatment of onycholysis on the legs of this type will also depend on eliminating the cause of its occurrence.
Diagnostics
To diagnose the disease and subsequent treatment, you should consult a dermatologist. If concomitant pathologies are detected, he can refer you to other specialists (allergist, gastroenterologist, endocrinologist, etc.).
To determine the method of treating onycholysis, the doctor should determine the causes of its occurrence. To do this, the doctor must examine the nail plates, collect anamnesis and evaluate accompanying symptoms, take tests for fungus, streptococci and staphylococci, and examine the blood to determine the general condition of the body.
In addition, it is possible to use other instrumental and laboratory methods, the choice of which depends on the possible causes of nail detachment.
Immediate causes of onycholysis
Detachment of the nail plate does not occur every time the patient is struck by an illness of one of the above systems. The main immediate causes of the development of pathology:
- poor trophism (nutrition) of the nail plate;
- violation of the innervation (nervous supply) of the plate;
- lack of vitamins (most often seasonal);
- regular trauma (in particular, detachment of the nail on the big toe is often observed after an injury while playing football).
Treatment
Treatment of fingernail or toenail disease that develops as a result of injury is easy to treat and depends on proper care. If an edge peels off, you should cut it off regularly with scissors until a new one grows back. To avoid subsequent damage, the plate should be sealed with an antibacterial tape. In cases where the nail injury is large, it can be surgically removed, after which a bandage is applied.
If the cause of onycholysis is a general disease, you should consult a doctor and begin treatment. Eliminating common diseases will gradually relieve you of brittle and peeling nails.
If the cause of the disease is the use of antibiotics, then the consequences of antibiotic therapy should be treated. Treatment will have to begin with intestinal dysbiosis. With this disease, microelements and vitamins necessary for nails are not absorbed in the small intestine. In this case, it is useless to take vitamins for nails until the dysbiosis is eliminated; the nails will be sore.
If you know that the cause of the disease was contact with chemicals, then you should wear rubber gloves when working with them.
When treating onycholysis, in the case of fungus, therapy is prescribed by a doctor depending on the condition of the body. In case of severe mycosis, treatment takes a long time (from 3 to 12 months), the mycologist prescribes systemic antimycotics, such as Itraconazole, Ketoconazole, Terbinafine, Fluconazole and others. You should also make nail baths with potassium permanganate, salt and soda every day.
It is possible to use special solutions for the treatment of onycholysis - a 1-2% solution of tinol or a 5% solution of chrysarobin in chloroform. After that, an antifungal cream is applied, which should be applied to the affected nail for 2 weeks, after which the affected area is easily filed off. The cream should be left under the patch overnight until the affected nail is completely removed, after which it is recommended to rub the cream into the nail hole daily for 3-4 weeks. This treatment is suitable for patients with dermatitis or eczema. Treatment should be continued until a healthy nail grows back.
For local treatment, antifungal ointments and solutions are used: Amorolfine, Bifonazole, Fukortsin, Exoderil and others.
Treatment of onychodystrophy at the Podology Clinic
The Podology Clinic, which is one of the largest technically equipped specialized complexes in Russia, offers to take advantage of the priorities of innovative medical technologies aimed at solving a wide range of problems of the feet and nails. Experienced podologists who master all known techniques have at their disposal the most advanced expert-class diagnostic and treatment equipment, ensuring the most accurate and painless correction.
If you have problems with your fingernails and toenails, you shouldn’t leave them to chance. Only a timely visit to a professional involved in the treatment of various onychopathies will help to identify and carry out full correction at the earliest stages, without aggravating the development of dystrophic changes. And don’t forget that nails play not only an aesthetic role, but are also an indicator of your health.
Video review of the PinPointe FootLaser laser and interview with Dmitry Zakharchenko (CEO) on the latest device for the treatment of onychodystrophy and onychomycosis:
Prevention
To prevent the disease, the following measures must be observed:
- When caring for your nails during a manicure or pedicure, avoid damaging them;
- Use quality coatings and nail polish removers;
- When working with household chemicals and other aggressive substances, wear rubber gloves;
- Eat right;
- Take vitamins;
- Treat chronic diseases in a timely manner.
We recommend visiting our Manicurist Forum , where you can ask questions or chat about interesting topics!
Other causes of illness
In addition to gross mechanical damage, there are other external factors that influence the onset of the disease. These include:
- failure to comply with hygiene rules;
- regular manicure;
- frequent use of acetone and other toxic substances;
- use of certain medications;
- influence of direct rays of the sun;
- lack of calcium and zinc in the body;
- carrying out cosmetic procedures under the influence of ultraviolet rays;
- high humidity.
Common causes of onycholysis are various cosmetic procedures and regular manicures. When using manicure tools, gel polishes and acetone, there is a possibility of damaging the nail. In addition, it is worth considering that care products such as varnishes, hardeners and remover contain aggressive chemicals that can harm the health of the nails. With regular use of such products, there is a risk of developing various diseases and brittle nails.