Causes of fingernail fungus
It has been proven that about 50 species of fungi can affect the nail plate on the hands, which are usually divided into dermatomycetes (dermatophytes), yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida and molds.
- About 80 - 90% of all cases of the disease are caused by dermatophyte fungi - Trichophyton rubrum, Epidermophyton floccosum, Trichophyton mentagrophytes gypseum, Trichophyton tonsurans and Trichophyton violaceum. The most common onychomycosis is caused by the fungi Trichophyton rubrum (70 - 90%) and Trichophyton mentagrophytes v.interdigitale (10 - 20%). The remaining dermatophytes account for about 3% of all cases of onychomycosis.
- From 5 to 10% of cases of the disease are caused by yeast-like fungi of the genus. According to European researchers, onychomycosis on the hands caused by this type of fungus ranges from 40 to 60%.
- Modern mycology notes a significant prevalence of nail damage by mold fungi. They are represented by different species belonging to the families Dematiaceae and Moniliaceae. In European countries, the most common molds are Aspergiluss scopulariopsis and Penicillium. spp, Scopulariopsis brevicaulis, Scytalidium spp, Acremonium spp and Fusarium spp. It is believed that they do not cause onychomycosis on their own. Fungi of this type penetrate into an already damaged nail plate, including yeast-like fungi and dermatophytes. Two types of molds - Scytalidium hyalinum and Scytalidium dimidiatum (Natrassia magniferae) are especially pathogenic and can independently cause disease. These pathogens are distributed mainly in countries with hot and humid climates.
Combined damage by different types of fungi and bacteria is very common. To clarify the diagnosis, laboratory confirmation should be obtained.
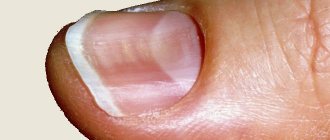
Rice. 3. Initial signs of fungal infection of the fingernails. The general appearance resembles a splinter.
Prevention of fungus during manicure
Manicure in a salon is one of the most common methods of infection. You need to carefully choose a specialist who not only has a good command of the coating technique, but also complies with all safety rules.
- Any tools must be processed after each client. However, an ultraviolet lamp or boiling cannot destroy all fungal pathogens. It is better if an autoclave or a dry-heat oven is used in the cabin.
- Disposable instruments or attachments must be opened immediately before the client.
- Before starting work, the master must wash his hands thoroughly.
- Clients’ hands must also be treated: first they are asked to wash them with soap, then wipe them with an antiseptic.
- The varnish must be applied using a disposable brush. The varnish itself should not be thick, and its composition should not contain formaldehyde and toluene.
At home, manicure tools should also be treated against fungus. It is necessary to accustom yourself to wipe all tools with an antiseptic before treating your nails and after the procedure. If you already have fungus, it is better to buy disposable paper files, which need to be changed with each procedure.
Epidemiology and risk factors for onychomycosis on the hands
Dermatophyte fungi
The reservoir and source of dermatophyte fungi is a sick person, from whom pathogens are transmitted through his personal belongings or through direct contact. The risk of infection increases if one of the family members has mycosis. In the chronic course of rubromycosis, the infection from the feet often spreads to the working hand and nails.
The infection is transmitted through the patient's personal belongings, including a towel, washcloth, shoes, manicure accessories, etc. Infection of the feet often occurs in swimming pools, saunas, showers, beaches and gyms. Red trichophyton lives for a long time on wooden floors and decking.
Risk factors:
- Diabetes mellitus and vascular diseases.
- The presence of diseases that weaken the immune system.
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Visiting beauty salons where infected instruments are used for manicure procedures.
- Nail injuries.
Rice. 4. About 80 - 90% of all cases of the disease are caused by dermatophyte fungi, of which 70 to 90% are caused by Trichophyton rubrum.
Yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida
Yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida are saprophytic flora. They constantly live in the body of a healthy person. Their development is inhibited by the normal functioning of the immune system. Active growth of fungi is promoted by long-term use of antibiotics, use of contraceptives, glucocorticoids and cytostatics, endocrine pathology (often diabetes mellitus) and other diseases. Pathogens enter the nails from the skin or lymphogenously. The disease often begins with inflammation of the periungual fold. Warmth and moisture are optimal living conditions for fungi of the genus Candida.
Risk factors:
- Humidity and elevated ambient temperature.
- Constant contact with water.
- Wearing false nails.
- Immunodeficiency states.
- Diabetes mellitus and vascular diseases.
- Failure to comply with personal hygiene rules.
Rice. 5. According to European researchers, onychomycosis on the hands caused by Candida fungi ranges from 40 to 60%.
Molds
Molds live in the soil. Their spores end up on food, things and environmental items. Mold onychomycosis does not spread among people. Fungi penetrate damaged nail plates from outside.
Risk factors include severe immunodeficiency and nail injuries.
Rice. 6. A risk factor for mold onychomycosis is wearing false nails and shellac (Shellac) - applying professional varnish and liquid gel.
Rice. 7. Lesions of nails by yeast-like fungi, mold fungi and Pseudomonas aeruginosa are similar to each other. To diagnose the disease, microscopic and microbiological examination is carried out.
Prevention
To avoid fungal or bacterial infection of the skin and nails, so that green nail syndrome does not occur, it is enough to follow simple hygiene rules.
- Use only your own shoes at home and away, do not give them to others and do not wear someone else’s.
- In public places, including beaches, bathhouses, sports locker rooms, do not walk barefoot.
- A patient with nail fungus is not recommended to walk around barefoot at home; he should have his own special means of care and personal hygiene - towels, scissors and nail files.
- You can protect your nails from infection, in particular green nail syndrome, by wearing comfortable shoes that are not tight and do not create a “greenhouse effect.”
- Healthy, well-groomed nail plates and skin are in themselves a protective factor against fungal and bacterial infections.
Nail structure and growth: what healthy nails and skin should look like, care rules
However, sanitary and hygienic measures cannot always provide a 100% guarantee of protection. It is difficult to foresee all variants of infection, especially if there are all the conditions for this: for example, wearing artificial nails for a long time, having a family member with nail fungus who has green spots on the nails, or visiting a gym, swimming pool, or bathhouse.
Mycostop - we analyze the line of drugs against fungus - indications, instructions for use, reviews
In order to prevent a possible disease, you can use antifungal and antibacterial agents: sprays, aerosols, creams, powders, etc. However, if signs of the disease have already appeared - green spots have appeared on the nails, you must immediately consult a doctor, do not wait for the infection to spread.
Hand antiseptics: application, application rules for manicure and pedicure
Structure and physiological characteristics of fingernails
The difficulties in treating onychomycosis are associated with the specific structure of the nail plate. This formation is a derivative of the epidermis and is a completely keratinized layer of horny cells. The nail is located on the nail bed and fits tightly to it. It has a distal (free) edge and a proximal one (the socket area is a light area at the base), surrounded by nail ridges, has a smooth and even surface, translucent vessels give a pink color.
The nail bed is a section of connective tissue on top covered with a layer of epidermis, which is the inner layer of the nail itself and makes up 1/3 of its thickness.
The growth of nail plates occurs due to the rapid proliferation (division) of keratocytes located under the root part - in the growth zone, called the matrix. Growth occurs from the proximal to the distal (free) edge. In 1 month, the fingernail grows by 2 - 4.5 mm (0.1 mm per day), on the toes - 1 mm per month (1.5 times slower).
Rice. 8. Structure of the nail: free (distal) edge (1), nail plate (2), nail hole (3), cuticle (4).
Mold on nails: tips and reviews
It is very unpleasant when mold appears on your nails. Advice and reviews will help you get rid of the disease once and for all. Use local treatment - this will help restore the nail and make it strong.
Go to an appointment with a dermatologist and carry out all the necessary examinations that the doctor prescribes. In parallel with treatment with folk remedies, follow the doctor’s recommendations.
IMPORTANT: A disease such as moldy nail fungus requires patience. After all, to obtain an effective result, treatment must be long-term.
Entrust your manicure hands only to trusted professionals who have everything necessary to disinfect tools and their workplace.
Do not put your nails in danger; if you have any defects or diseases, avoid manicure for a while. Be healthy!
Paths of penetration of fungi and forms of onychomycosis
“Agression factors”, represented by proteolytic enzymes, promote the penetration of pathogens into the nail plate. Keratinase decomposes proteins into peptones and amino acids, which ensures their consumption by fungi, and also promotes the rejection of the epidermis from the dermis and the melting of tissues, as a result of which pathogens freely penetrate between the layers of keratin. Constantly high temperature and humidity are necessary conditions for the development and growth of fungi.
Pathogens penetrate the nail from the distal edge, through its outer part or the proximal nail fold.
There are several forms of onychomycosis:
- Distal or distal-lateral (lesion from the free or lateral edge).
- White superficial (infection occurs directly through the nail plate).
- Proximal (subungual).
- Total dystrophic.
Rice. 9. Different forms of onychomycosis: lateral, proximal, white superficial and total.
Distal and distal-lateral form
Distal and distal-lateral forms of onychomycosis are the most common. They are most often caused by the fungi Trichophyton rubrum.
Pathogens penetrate the nail plate from the free edge or side fold. The pathological process develops in the nail bed, where cellular proliferation (cell reproduction) is activated, which leads to tissue proliferation - the formation of subungual hyperkeratosis. The nail begins to separate from the nail bed, loses its transparency, acquires a whitish or yellowish color, becomes thinner, begins to crumble and deteriorates over time. In the case of pronounced hyperkeratosis, the nail plate appears thickened. The pathological process spreads towards the proximal edge.
Rice. 10. Distal form of onychomycosis on the hands.
Rice. 11. Distal and distal-lateral routes of infection.
Rice. 12. Lateral form of onychomycosis on the hands.
White superficial onychomycosis
Damage to the nail plates on the dorsal side (upper surface) occurs when infected with fungi with pronounced keratolytic ability, which is noted when infected with the fungi Trichophyton mentagrophytes var. interdigitale. They destroy the nail much less frequently, but more strongly and faster than Trichophyton rubrum. Fungi, under the influence of keratinase enzymes, perforate the stratum corneum with hyphae, gradually capturing all layers of the nail plate, on which stripes and opal-white spots appear. The surface becomes mealy, rough and loose, and is easily scraped off. Thickening and separation from the nail bed does not occur. The matrix is not involved in the pathological process. Fungi Trichophyton mentagrophytes var. interdigitale most often affects the nail plates on the toes, on the hands - in isolated cases.
Rice. 13. White superficial onychomycosis.
Proximal (subungual) onychomycosis
This form of onychomycosis on the hands is rare. Fungi penetrate the nail plate from the nail fold. A white spot appears in the area of the socket (proximal edge), gradually spreading to the free edge. When viewed using magnifying optics, a “branching network of tunnels” is revealed.
Fungi remain in the matrix or penetrate the nail bed and cause degenerative changes over time. Hyperkeratosis does not develop. When the nail bed is damaged, grooves, irregularities and cracks appear. Over time, the nails are completely destroyed.
- The cause of proximal onychomycosis on the hands is the yeast-like fungi Candida albicans (more often) and Trichophyton rubrum (rarely). The disease begins with inflammation of the proximal ridge (paronychia). It swells, thickens and turns red. The cuticle separates from the surface of the nail and the fungi freely penetrate into the matrix and nail bed, eventually causing damage and detachment of the nail from the tissues of the finger.
- The proximal form of onychomycosis on the hands occurs in cases where, during cosmetic correction, the eponychium, which occupies the space between the posterior skin fold and the nail plate, is removed.
- The disease often occurs in HIV-infected patients when the infection spreads through the blood vessels.
Rice. 14. Proximal (subungual) onychomycosis.
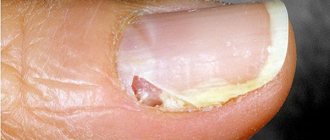
Rice. 15. The initial stage of damage to the fingernails due to candidiasis. The disease often begins with inflammation of the posterior cushion.
Total onychomycosis on the hands
With a long course of the disease, total onychomycosis develops, when the nail plates are completely affected, and dermatophyte fungi penetrate into the connective tissue thickness of the nail bed and even into the bone marrow canal. In such cases, there are cases of recurrent course of the disease even when the fingernail is removed in the absence of systemic antifungal therapy.
Rice. 16. Destruction of the nail plates during long-term onychomycosis. In the photo on the right there are threads of mushrooms in the lumen of the medullary canal of the phalanx of a finger on the hand.
Damage by mold fungi
It is believed that mold fungi cannot infect the nail plate on their own. They penetrate into it through cracks and colonize empty vessels and spaces between the ridges. The disease occurs with the development of hyperkeratosis and slow destruction of the nails. The mold fungi Scytalidium dimidiatum and S. hyalinum independently cause onychomycosis on the hands, mainly in people living in countries with tropical and subtropical climates.
Rice. 17. Different forms of onychomycosis on the hands of one patient.
Green manicure fashion trends 2021
With fashion trends 2021, everything is quite simple. As always, rhinestones and stones are popular, only this season they are laid out in the form of imitation jewelry. This type of nail decor is called inlay. Various rubbings are also in fashion, with the help of which you can create a mirror surface or a shimmering effect on the surface of your nails. Acrylic powder does not lose its popularity. It is often used to create a shimmering geometric stripe gradient.
Creative masters of beauty salons create real masterpieces with the help of varnishes and gels. There are several striking examples using Vinylux on the page of one of the beauty centers, here. Frankly, it is unlikely that you will be able to repeat the design yourself: it is inconvenient to apply the design to yourself and it requires experience and artistic taste. Therefore, it is easier to come to the specialist with photographs of the designs you like.
A fashionable botanical manicure will be a real hit next summer. The once popular branches will be replaced by lush tropical foliage, which you can paint with a brush yourself or, if desired, use suitable decals.
The marble design, which in green design resembles the texture of semi-precious stones such as malachite or serpentine, will not lose its relevance.
A green manicure done in a cat's eye style looks amazing. And to give it even greater expressiveness and depth and expressiveness of the color of the manicure, many masters cover it with a finishing layer of stained glass varnish. It creates a glass effect. This simple but effective technique can be used to create a New Year's manicure.
A manicure with green polish with a geometric or minimalist pattern will not be forgotten either. The trend of the season is an ornament of chaotically intertwined thin stripes or a decor in the form of a wide vertical stripe on the ring finger.
Types of onychomycosis on the hands
There are normotrophic, hypertrophic and atrophic (onycholytic) types of lesions.
With the normotrophic type of lesion, the nail retains its thickness and shine, only the color changes - from white to ocher-yellow. Changes appear on the lateral surfaces (laterally), where stripes and spots appear. Gradually the entire nail plate is affected, except for the lunula area. There is no brittleness or crumbling.
Rice. 18. Normotrophic type of lesion.
With the hypertrophic type of lesion, subungual hyperkeratosis develops, the nail plate becomes dull, loses its shine, acquires a brown color, thickens, partially collapses, and the edge becomes pitted. The lunula area is not affected for a long time.
Rice. 19. Hypertrophic type of lesion of fingernails.
With the atrophic type of lesion, the nail plates quickly separate from the nail bed, remaining smooth, but become dull, flat and thin, acquire a whitish-yellow color, and are partially destroyed over time.
Rice. 20. Atrophic type of lesion of the nails on the hand.
Signs of onychomycosis on the hands
The main signs of damage to fingernails are changes in color, shape and thickness.
- When infected with red trichophyton and some types of mold fungi, the nail plates become yellow in color; when infected with the fungi Trichophyton mentagrophytes var. interdigitale - white, when affected by mold fungi - green, brown, brown or black.
- With an increase in the amount of horny masses (subungual hyperkeratosis), the nail appears thickened.
- With a long course of the disease, the nail plates crumble and collapse.
Rice. 21. Changes in the color and shape of the nail plates.
Rice. 22. Changes in the color of nails when affected by different types of fungi.
Rice. 23. Yellow color of nails due to Trichophyton rubrum infection.
Rice. 24. View of the nail plates on the hands when infected with Candida albicans fungi.
Rice. 25. Mold onychomycosis.
Features of onychomycosis on the hands caused by dermatophyte fungi
Fingernails are affected by dermatophytes in 40 - 60%. The most common are Trichophyton rubrum (70 - 90%) and Trichophyton mentagrophytes v.interdigitale (10 - 20%). The remaining dermatophytes account for about 3% of all cases of onychomycosis. The reservoir and source of pathogens is a sick person. Dermatophytes survive in the environment for more than 2 years. They live in sand, pebbles, stones, on old and diseased trees, wooden flooring, seats and trestle beds.
With rubrophytosis, a hypertrophic type of lesion, distal and distal-lateral form, is more often noted. In 25% of people suffering from mycosis of the feet for a long time, the infectious process spreads to the skin and nails of the working hand first, and then to the second hand.
For epidermophytosis, caused by the fungi Trichophyton mentagrophytes var. interdigitale, fingernails are extremely rarely affected. Pathogens have a pronounced keratolytic ability and quickly destroy the surface of the nail plate (white superficial onychomycosis). Its surface becomes loose and rough, opal-white in color. Mycosis occurs without hyperkeratosis and involvement of the matrix in the pathological process.
With trichophytosis, fingernails are rarely affected. The cause of mycosis is often the anthropophilic fungi Trichophyton tonsurans and Trichophyton violaceum, much less often - Trichophyton mentagrophytes v.gypseum and Trichophyton verrucosum.
When infected with anthropophilic trichophytons, the nail plates on the hands are affected long after the damage to the scalp. At the site of pathogen penetration, a rounded gray-white spot appears in the thickness of the nail plate - the only sign of the disease that exists for a long time. The nail remains shiny and smooth for a long time, but later becomes dull, dirty gray, lumpy, and crumbles easily. In some cases, the posterior cushion becomes inflamed, it becomes swollen and reddish-bluish. The disease lasts for many years.
When infected with zoophilous trichophytons, the nail plates are affected only on the hands, mainly their superficial layers. Inflammation of the nail folds is noted, blisters and peeling appear on them.
Rice. 26. The initial stage of fingernail fungus.
Features of onychomycosis on the hands caused by yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida
The second most common lesions of fingernails after dermatophytes are yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida. The incidence of damage according to European researchers ranges from 40 to 60%. Among yeast-like fungi, in 90% of cases the cause of the disease is Candida C. albicans, much less often - C. tropicalis, C. parapsilosis and C. guilliermondii.
Nail plates are 3 times more likely to be affected by Candida fungi in women whose profession is related to cooking and confectionery production, and cannery workers. Predisposing factors are trauma, maceration, high humidity, wearing false nails, diseases that weaken the immune system, diabetes and vascular diseases.
The disease begins with inflammation of the posterior periungual fold, which swells, the skin over it becomes hyperemic, thins and becomes shiny. The nail skin disappears. The edge of the nail fold hangs over the nail plate. When pressed, pus of a crumbly consistency is released from under it. Gradually, the lateral ridges become involved in the inflammatory process, and the pain becomes severe and throbbing. The areas of the nail corresponding to the nail folds become soft, acquire a white, brownish-brown or green color, and gradually separate from the nail bed. Wave-like transverse grooves form on the nail plate. In some cases, the nail plate becomes thinner and is rejected, which is observed when fungi penetrate into the matrix and nail bed. The disease tends to be chronic.
Onychomycosis on the hands occurs with chronic candidiasis. The disease begins in childhood. The leading cause of mycosis development is hereditary immune disorders. Nails become significantly thicker with the disease. The inflammatory process is weakly expressed. The nail skin is preserved. The fingers at the ends become like drumsticks.
Candidal paronychia should be distinguished from psoriasis, lichen planus, eczema, pyococcal paronychia, nail damage due to rubromycosis, onychomycosis, trichophytosis and mold mycoses.
Rice. 27. Candidiasis begins with inflammation of the posterior nail fold.
Rice. 28. Damage to the periungual fold and fingernails due to candidiasis.
Rice. 29. Onychomycosis on the hands with chronic candidiasis.
Rice. 30. Candidal onychomycosis on the hands of a child.
Rice. 31. Wearing false nails contributes to the development of onychomycosis on the hands.
Features of onychomycosis on the hands when affected by mold fungi
Modern mycology notes a significant prevalence of mold onychomycosis. It is believed that most molds do not cause disease on their own. They penetrate already damaged nail plates, including yeast-like fungi and dermatophytes. Two types of molds - Scytalidium hyalinum and Scytalidium dimidiatum (Natrassia magniferae) are especially pathogenic and can independently cause nail damage. These pathogens are distributed mainly in countries with hot and humid climates.
Molds produce proteolytic and keratolytic enzymes, thanks to which they are able to penetrate through the nail plate into the nail bed. They cause subungual hyperkeratosis and slow destruction of the nail plates, which in the course of the disease turn black (Scytalidium spp.), green or gray (Scopulariopsis brevicaulis). Molds most often affect the toenails, especially the first ones. The process proceeds very slowly without damaging the periungual ridges.
Rice. 32. Mold onychomycosis. The cause of the disease is the fungi Scytalidium spp.
Rice. 33. Mold onychomycosis on the legs (more common) and arms (less common). The cause of the disease is Aspergiluss scopulariopsis
Rice. 34. Damage to the nail plates by mold fungi.
At the slightest suspicion of fingernail fungus, the diagnosis should be confirmed by the results of microscopic and cultural examination methods.
Mold under the nail: folk remedies for treating nail fungus
After removing the extended nail, refrain from any manipulation of the nails. Perform only therapeutic procedures that help restore the nail plate. Folk remedies for treating nail fungus will help remove mold.
IMPORTANT: First, visit the salon and remove your nail extensions!
After this, you can begin treatment with folk remedies that will help make the nail plate strong and healthy.
RECIPE: Dissolve half a teaspoon of baking soda in a glass of warm boiled water. Lubricate the nail plate with this solution. After the soda water has dried, apply celandine oil.
If you buy birch tar at the pharmacy, then you can prepare an effective remedy.
RECIPE : Steam your hands in a basin with warm soapy water (use laundry soap). If your nails are long, cut them. Spread the nail plates with birch tar. If possible, do not wash off this substance for 2-3 hours. Do this procedure every day and after a couple of weeks you can forget about moldy fungus on your nails!
Fungal infection does not like alkaline and acidic environments. Therefore, you can come up with your own recipes and alternate treatments for greater effectiveness.
TIP: Use lemon or apple cider vinegar as ingredients for nail masks.
Diagnosis of the disease
At the first signs of nail damage, you should immediately consult a dermatologist. Timely detection of the disease is the key to successful treatment.
In order to establish and confirm the diagnosis of onychomycosis, microscopic and microbiological research methods are carried out.
- Microscopy reveals the fact of fungal infection.
- Microbiological examination determines the type of fungi.
- Currently, a new method for diagnosing fungal diseases has been developed - PCR, which makes it possible to identify the pathogen in a matter of minutes with an accuracy of up to 80%.
It must be remembered that the cause of damage to the nail plates is often associations of pathogens - dermaphotitis + yeast-like and/or mold fungi in combination with bacterial flora.
Rice. 35. View of the main causative agents of onychomycosis under a microscope - the dermatophyte fungi Trichophyton rubrum (photo on the left) and the round-shaped budding cells of the yeast-like fungi Candida albicans.
Rice. 36. Growth of the fungal culture Trichophyton rubrum (photo on the left) and Candida albicans (photo on the right) on nutrient media.
Differential diagnosis
Fingernail fungus should be distinguished from a number of infectious and non-infectious diseases.
Rice. 37. Lesion with psoriatic arthritis (photo on the left) and Pseudomonas aeruginosa (photo on the right).
Rice. 38. View of fingernails after chemotherapy (photo on the left) and psoriasis (photo on the right).
Rice. 39. Post-traumatic onychomycosis.
Rice. 40. The photo shows nails with Wilson-Konovalov disease. The blue color is due to an excess of copper in the body.
Rice. 41. Lesion in melanoma (photo on the left) and lichen planus (photo on the right).
Rice. 42. Damage to the skin and nail plates due to eczema.
Causes of mycosis infection, risk groups
Salons that provide nail extensions must adhere to certain rules regarding the disinfection of tools in their work. In its absence, infection may occur. Among the main violations are:
- improper treatment of manicure accessories and work surfaces from pathogenic microorganisms;
- insufficient ventilation of the master's place in the cabin;
- lack of professionalism, negligence of a specialist;
- violations in the implementation of the procedure;
- mismatch between the extension material and the plate, which creates a small space suitable for the spread of fungus;
- the presence of mycosis of the legs, arms;
- low-quality gels and cosmetics.
Both women and men are not immune from fungus. The risk of developing mycosis increases with age. But most often the disease can develop after an increase in the weakened immune system.