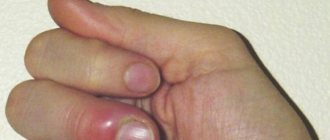
A bruise under the nail always forms after a blow, compression, or pinching; it can be provoked by some internal pathologies - diabetes, melanoma, diseases of the cardiovascular system. It is important to understand the true cause of the hematoma, to exclude bone fractures - this is done by a traumatologist.
Any bruise under the nail goes away in 7-14 days, depending on the extent of the injury. Hematoma is treated by using ointments (Tetracycline, Ichthyol, Heparin), painkillers (Analgin, Ibuprofen). Traditional methods are also effective - baths, compresses, lotions.
What causes a bruise under the nail?
A bruise under the nail always forms against the background of the presence of provoking factors; independent hemorrhage in this place is impossible; the reasons for the appearance of a hematoma are:
- a strong blow directly to the finger;
- compression of the foot in the nail area - for example, when wearing tight shoes frequently/constantly;
- fungal disease in an advanced form, which occurs with detachment of the nail plate from the bed;
- pinched finger;
- playing football in shoes that are not directly intended for this event;
- forced long-term use of medications that affect the level/rate of blood clotting;
- wearing specific shoes, which is typical for skiers and skaters;
- active progression of diabetes mellitus, melanoma, heart pathologies, fragility of blood vessels;
- features of the anatomical structure of the foot - for example, if the second toe is much longer than the big one.
The formation of a bruise begins no earlier than 1-2 hours after the injury, until this moment there is swelling of the tissue at the site of impact/compression and redness of the skin. The hematoma itself forms only after blood begins to leak from the vessels if they burst during damage. Then the bruise develops as follows:
- a small pink spot forms;
- the nail bed, in whole or in part, is painted in a dark red/crimson shade;
- the nail plate becomes blue, the person complains of pain and a feeling of numbness;
- a large purple spot forms, the pain becomes minimally pronounced;
- after a few days, the bruise acquires clear boundaries, its area becomes smaller, pain is present only when pressing on the hematoma;
- 7 days after the injury, the bruise becomes black and decreases in size.
On the foot
On the leg, a bruise under the nail forms against the background:
- kicking while walking;
- heavy objects falling on fingers;
- wearing narrow, tight shoes.
The last provoking factor is “triggered” most often - uncomfortable shoes put pressure on the foot, and a bruise especially often forms under the big toe nail. Such hematomas are small in size and painful.
A bruise can also form after an unsuccessful pedicure, when the master cut the edge of the nail too carelessly and as it grows, it begins to cut into the soft tissue.
On the hand
On the hands, hematomas under the nails occur for the same reasons as on the lower extremities - a blow to the finger in the area of the nail plate, pinched fingers, falling heavy objects.
Hematomas can form in women when wearing decorative gel polish for a long time - it clogs the nail plate and prevents the access of oxygen. The result will be a disruption of all metabolic and regenerative processes, increasing the fragility of blood vessels.
Spontaneous bruises under the nails may appear on both the feet and hands if a person has diabetes. This symptom is often the only one indicating an imbalance in blood sugar levels, so people with hematomas need to be examined and find out the true cause of their appearance.
When it's not blood under the nail, but a mole
The appearance of a bruise can be similar to a mole if it is located under the nail - this is not blood, but a completely normal formation that requires control over its size in order to prevent the degeneration of its benign cells into malignant ones.
The difference between a mole under the nail and a full-fledged bruise:
- constantly present;
- does not change color;
- has clear boundaries and does not change its size;
- there is no pain even with strong pressure on the false hematoma.
How long does it take?
A bruise under the nail goes away on average in 1 week. But it all depends on the size of the hematoma - a large one can disappear in 10-14 days, a minimal one - in 2-3 days after formation.
Why do they appear?
A bruise under the nail is formed under the influence of the following factors:
- mechanical impact (heavy objects falling on the leg, pinching of the nail phalanges);
- fractures of the nail plate and foot bones;
- wearing tight shoes for a long time (constant pressure is placed on the big toe, which leads to blood stagnation and damage to the subcutaneous vessels);
- occupational deformation (bruises on the nails of the big toes appear when wearing winter ski shoes and skates that put excessive pressure on the forefoot);
- administration of drugs that reduce blood clotting (liquid blood seeps through the walls of blood vessels, forming hematomas);
- dysfunction of the cardiovascular system (blood supply to tissues is disrupted, the condition of the vascular walls worsens);
- malignant tumors of the skin and bones;
- diabetes mellitus;
- fungal infections accompanied by detachment of the nail plate.
Important information: How to treat a hematoma during pregnancy and why bruises appear on the abdomen
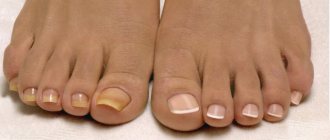
What does a subungual hematoma look like?
Subungual hematoma has specific symptoms:
- severe throbbing pain at the site of injury;
- formation of a bluish-tinged spot;
- the formation of severe swelling, swelling of the injured finger;
- inability to move a finger normally;
- feeling of numbness in the finger, foot.
The bruise gradually changes its color - first there are red shades, then they turn into purple and dark blue.
If a subungual hematoma is caused by wearing narrow, tight shoes, then there is no pain syndrome. It appears only when pressing directly on the bruise.
How does a hematoma form?
2-3 hours after the mechanical impact, a bruise begins to form under the nail. Subungual hematoma goes through the following stages in its development:
- Swelling of soft tissues and skin. At this stage, there is still no bruise on the nail; it appears after a rupture of the vascular wall with hemorrhage under the nail plate.
- The appearance of a pink spot. The periungual areas become crimson in color, and the nail turns blue. At this stage, the sensitivity of the finger decreases and pain is felt.
- Formation of a large purple spot. At this stage, the severity of pain decreases.
- Blue discoloration of the hematoma. The bruise acquires clear boundaries and its diameter decreases. Pain appears only when pressed; there is no discomfort at rest.
- Disappearance. After a week, the spot under the nail turns black and sharply decreases in size. The boundaries of the hematoma remain pronounced, there is no pain. Within a week, a bruise on the leg may resolve spontaneously.
Diagnostics
If a hematoma forms, you should definitely seek help from a traumatologist - a bruise may indicate a fracture or cracks in the bones, which may not heal properly without proper treatment. A traumatologist treats hematomas, but first he will conduct a diagnosis:
- visual inspection of the damaged finger;
- asking the patient about the time of appearance of the bruise under the nail and what it may be connected with;
- referral for laboratory testing of blood and urine;
- X-ray of the limb to exclude fractures.
If there are symptoms of purulent inflammation at the site of the hematoma, then a scraping of biological fluid is taken to identify the causative agent of the pathological process - this is necessary for the competent prescription of antibacterial drugs.
Opening the nails
If a large hematoma appears under the nail, then you need to go to a medical facility to remove the blood that has accumulated in a large volume. But this type of assistance is effective until it collapses. The nail plate is perforated using a special drill or removed surgically.
For such purposes, a medical needle or wire heated by a burner is used. Using a hot needle, the tissue structure melts without pain or blood loss. After the operation, the finger is bandaged with a sterile bandage, and after a while the plate will slide off. This treatment method will allow the new nail to grow faster. Sometimes after the procedures the use of antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs is prescribed.
Treatment of subungual hematoma
If the bruise is small, then the nail plate is treated with an antiseptic; in case of extensive lesions, the subungual hematoma is treated with specific medications. preference is given to external agents - ointments based on anticoagulants, antibiotics, anti-inflammatory substances.
It is quite advisable to use traditional methods as part of therapy. They will help you quickly and safely get rid of a hematoma if the use of medications is contraindicated or unavailable.
Surgical intervention, namely nail removal, is indicated only for serious injuries. It is carried out in an outpatient clinic, hospitalization is not required.
What to do when there is dried blood immediately after a bruise
If immediately after a bruise there is dried blood under the nail, then you should do the following:
- Make sure there are no broken bones. To do this, the injured finger needs to be bent and straightened several times in a row - the presence of acute pain makes it necessary to visit a doctor at the emergency room.
- Place your finger under cold water, apply any frozen product or very chilled product from the refrigerator to it. Cooling procedures last a maximum of 25 minutes; every 5 minutes you need to release your finger from the “oppression” for 1-2 minutes.
- If there is damage to the skin, then the wound must be washed and treated with an antiseptic - a solution of iodine, brilliant green, Miramistin. This will prevent infectious agents from entering the wound and the development of a purulent process.
- An injured person can take a painkiller - Ibuprofen, Analgin and others, if there are no individual contraindications for this. This will relieve acute pain and eliminate discomfort.
- Apply a tight pressure bandage or adhesive plaster to the finger. This will prevent the nail plate from peeling off and being pulled away from the nail bed.
How to release liquid
In order for the bruise under the nail to disappear as quickly as possible, you need to release the liquid from the subungual space:
- pierce the location with a needle - small, disinfected or sterile from a syringe;
- release the blood through the puncture hole - you can slightly speed up the process by pressing on the nail if the pain intensity level allows it;
- bandage the finger with a bandage, laying a gauze pad or cotton pad soaked in antiseptic.
The best option is to consult a doctor for the procedure in order to exclude the development of complications such as wound infection and the development of an inflammatory, purulent process.
Watch the video on how to remove a hematoma under the nail:
How to help your child
If a child develops a hematoma after a bruise on a finger under the nail, then he can only be helped in terms of pain relief:
- place the injured finger in the cold;
- give an age-appropriate pain reliever;
- treat the wound with iodine or Miramistin;
- apply a tight pressure bandage.
In childhood, it is forbidden to independently pierce a hematoma to remove fluid, remove an already exfoliated nail, or trim it if it has split due to an impact. You can get an infection, and the pain threshold in children is much lower than in adults - there is no need for unnecessary pain.
How to clean at home
At home, you can quickly remove a bruise under the nail using folk remedies:
- Combine dry plantain and yarrow leaves in equal proportions. Take 1 tablespoon of the mixture, pour 100 ml of boiling water and leave in a sealed container for 2 hours. Squeeze the raw material from the cake, fold it into gauze and apply to the site of the bruise. The application time for the lotion is 30 minutes; this procedure should be performed 2 times a day.
- Take 1 tablespoon of badyagi powder and add warm water to it in such an amount that when stirred, a homogeneous, paste-like mass is obtained. It is applied to the damaged finger in a thick layer and left until completely dry. Wash off the “mask” with a decoction of chamomile flowers, prepared according to the classical method (1 tablespoon per 200 ml, simmer in a water bath for 5 minutes). The frequency of the procedure is 3 times a day.
- Combine 1 tablespoon each of table salt and baking soda, pour into a container with 200 ml of warm water, dissolve. Place the finger with the hematoma under the nail into the liquid and leave for 10-15 minutes. After the procedure, the finger is dried and treated with a solution of hydrogen peroxide. At least two such manipulations should be performed per day.
- Combine 2 tablespoons of dry red wine, 2 tablespoons of table vinegar 6% and 1 teaspoon of sea salt, stir everything. Moisten gauze folded in several layers in the prepared mixture, squeeze lightly and apply it to the injured finger as a compress. The exposure time is 2 hours, the procedure is carried out 2 times a day - morning and evening.
Effective folk methods for treating a bruise under the nail include:
- Applying a white cabbage leaf to the injured finger. This will relieve the throbbing pain, but the leaf must first be “beaten off” with the blunt side of a knife.
- Using lotions with a solution of manganese and then rinsing the nail with tincture of wormwood. This will relieve pain and speed up the process of hematoma resorption. The lotion is applied for 10 minutes, the tincture is bought at the pharmacy.
- Application of compresses made from chopped onions. Add 1-3 drops of tea tree oil to the pulp, wrap the mixture in gauze and fix it on the finger with a bandage. The exposure time is 25-30 minutes, the procedure speeds up the process of getting rid of the bruise.
3 days after injury, you can begin thermal procedures. To do this, you need to dissolve 1 tablespoon of salt, the same amount of baking soda and 1 teaspoon of an alcohol solution of iodine in 2 liters of warm water. Place the foot or hand with the injured finger in the bath for 15 minutes, then wipe everything dry and treat the wound with Tetracycline ointment, castor oil emulsion or hydrogen peroxide.
Medicines for bruising
For bruising, external agents are used that have anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antibacterial properties, these include:
- Ichthyol ointment;
- Levomekol;
- Sintomycin;
- Vishnevsky ointment;
- Tetracycline ointment.
They are applied directly to the site of the injury in a thick layer, covered with a bandage on top and secured with a bandage or adhesive plaster. The bandage is changed 2 times a day. Heparin ointment will also be effective, which doctors recommend using when an abscess forms at the site of injury with purulent contents. The drug is applied to a cotton pad, which is then fixed on the finger.
To relieve the most severe throbbing pain, you can use a “compress” of Dimexide and Novocaine - the agents are combined in a ratio of 1:3, respectively, a gauze cloth is moistened in the mixture and applied to the bruised area. You can keep the “compress” until the pain completely disappears.
Disinfectants
It is important to treat the wound and the nail, if it has fallen off, with an iodine solution. In the absence of the latter, you can use vodka or alcohol, but it is important to be careful with the volume of liquid. These products dry out the skin, so you should not use them in large quantities. This also applies to greenery.
You can use 3% hydrogen peroxide. It must be borne in mind that treatment of nail separation with iodine is also considered effective. You can treat the damage with castor oil emulsion. The product has a hemostatic, anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect. From the 3rd day of resorption of the hematoma, heparin ointment and arnica can be used. Treatment with these agents involves treatment several times a day.
At night you can apply compresses with Dimexide (5-7 days). The substance is diluted with novocaine (0.25%) in an amount of 1:3. Then gauze is dipped in the solution and applied to the affected area. Place cling film or polyethylene on top and secure everything with a bandage. The compress should be removed after half an hour.
Bodyaga has an effective effect. The powder is diluted with water to form a paste. The product is applied to the wound. You can also buy bodyagu in the form of an ointment.
Why is subungual hemorrhage dangerous?
Subungual hemorrhage is dangerous if no therapeutic measures are taken, as complications may develop:
- infection of the subungual space, which is accompanied by the formation of an abscess with purulent contents and the development of a pronounced inflammatory process;
- deformation of the nail plate, which will grow back in place of the damaged one, which makes it necessary in the future to remove the nail to obtain a smooth and healthy plate;
- detachment of the nail plate even with minor hematomas - surgical removal will have to be performed to obtain a new stratum corneum.
If the infection goes undetected, the process may result in necrosis of the soft tissues of the finger and its complete amputation.
Danger of hematomas
Every bruise, no matter how minor, must be treated. The accumulation of blood, ichor or pus under the nail can have serious consequences:
- infection, blood poisoning;
- nail detachment;
- deformation of the stratum corneum;
- loss of a finger due to severe infection.
If the pain does not go away within 24 hours, the swelling grows, and pus accumulates under the nail, you should go to the emergency room. Serious injuries to the limbs and nail plate are treated only after consultation with a doctor.
Precautionary measures
To prevent the formation of hematomas in the subungual space, you should follow the recommendations of doctors:
- wear comfortable shoes that fit exactly;
- trim your toenails short;
- take breaks of 3-6 months when applying gel polish manicure;
- lift heavy objects and perform physical work in strict accordance with safety regulations;
- take vitamin C courses to strengthen the walls of blood vessels;
- try to avoid household injuries.
A bruise under the nail is not dangerous if immediately after the injury the damaged area was properly treated, and treatment is carried out using both medications and folk remedies. In case of severe injury, it is important to immediately consult a doctor to exclude a fracture and prevent infection from entering the wound.
A bruise under the nail always forms after a blow, compression, or pinching; it can be provoked by some internal pathologies - diabetes, melanoma, diseases of the cardiovascular system. It is important to understand the true cause of the hematoma, to exclude bone fractures - this is done by a traumatologist.
Any bruise under the nail goes away in 7-14 days, depending on the extent of the injury. Hematoma is treated by using ointments (Tetracycline, Ichthyol, Heparin), painkillers (Analgin, Ibuprofen). Traditional methods are also effective - baths, compresses, lotions.
What is prescribed?
Although first aid has been provided, it is necessary to continue treating the hematoma under the big toe nail. Doctors usually prescribe medications that allow swelling to resolve faster. If there is pain, the following medications are prescribed:
- "Analgin";
- "Ketanov";
- "Ketorolac".
If the nail peels off, the wound should be washed, ointment applied and a bandage applied. Such drugs as Venitan, Troxevasin, and Venoruton are often used. After eliminating the hematoma and reducing the pain, it will be possible to assess the condition of the finger and nail. Doctors often identify bruises and fractures, which is why the bruise appeared.
If there is a suspicion of a toe fracture with a hematoma under the big toe nail, it is recommended to immediately consult a doctor rather than use home methods. The phenomenon when a bruise appears for no apparent reason is also considered dangerous.
Treatment
It is necessary that the treatment of subungual hematoma be carried out by doctors. Let's consider the features of the treatment process. First, iodine is taken and the nail is treated. (Other disinfectants may also be used.) Then the nail is punctured using a hot needle in the area where the greatest amount of blood accumulation is observed. (This place is usually the most convex).
Nail piercing
As a result, blood begins to be released. If not, you should gently press down on the edge of the nail. After removal of the subungual formation is completed, the patient is given a cool bandage. Instead of a bandage, you can also take, for example, ice and place it on a clean, dry napkin. Then the nail plate is treated with a disinfectant again, and the bandage is placed on the finger.
This method of therapy for subungual hematoma promotes the release of blood, which promotes rapid healing and makes the affected area less painful. Using this method, treatment does not cause pain, because there are very few nerve endings in the nail. It is worth noting that it can cause the development of inflammation and the addition of some infections. But if the specialists do everything correctly, you won’t have to worry about anything.
Remember, if the subungual hematoma was under the toenail, you need to do this procedure without wearing shoes or find a fairly loose and comfortable model.
Traditional methods of treatment
A bruise under the nail (that is, hematoma) can be cured using many effective folk remedies. Let's consider several treatment options.
- You can use plantain, because it eliminates pain and relieves inflammation. A thin plantain leaf is applied to the affected area.
- It is very easy to prepare a tincture of lemon balm for compresses. You need to take 4 tbsp. l. lemon balm herbs, pour 400 ml of boiling water. Leave for half an hour, then start applying compresses.
- Subungual hematoma is treated with ordinary onions. Onion juice is combined with the resulting mushy mass and applied to the diseased nail.
- St. John's wort can be used. A decoction is prepared from it and used internally. Recommended dose – 1 tbsp. l. three to four times a day. In addition, the decoction is often used as a means of applying compresses.
Take care of the condition of your nails! Try to avoid injuries, give preference to loose shoes, and eat foods enriched with vitamins and microelements. If you suspect you have a subungual hematoma, consult a doctor, let him examine you, advise the correct diagnosis and treatment!
Diseases with the same symptoms
In essence, a subungual hematoma on the big toe or hand is an absolutely safe disease. In the first days, of course, it causes some discomfort, like any other bruise, but it does not cause any real harm to health. Much more unpleasant is that some serious diseases can have similar symptoms. When you discover a dark spot on your nail, it is very important to conduct a thorough diagnosis, as well as analyze the past for any injuries.
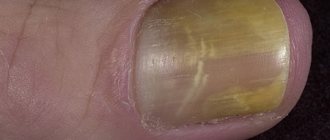
In particular, local darkening of the nails can be caused by a fungus in the later stages of its development. Such spots can be of very different types, but they all resemble hematomas at one or another stage of development. Since they do not appear at the beginning of the disease, it is quite possible to conduct a high-quality and complete diagnosis. If you remember for sure that you have not had any injuries relatively recently, then it is very likely that the disease is caused by a fungus.
Bruising under your toenails remains very painful for almost a week after the injury. Even if your finger itself is almost undamaged, the nail will still hurt when pressed, or severe throbbing pain will be constantly present. The fungus, although it can cause mild pain, does not remind itself so much and is characterized mainly by itching.
If, in addition to the blue plate, you notice at least some of the signs listed below, then you should consult a doctor to treat nail fungus. All these signs directly or indirectly indicate the disease.
- Skin itching;
- Peeling of the skin;
- The appearance of painful cracks between the fingers;
- Brittleness and fragility of the nail;
- Plate delamination;
- Unpleasant odor;
- Yellowing or blue discoloration of the plate.
Also, a blue nail may indicate the presence of cardiovascular diseases. Usually, in this case, the nails turn blue completely and all at once, which occurs as a result of insufficient saturation of the fingertips with oxygen. In this case, all fingertips acquire a bluish tint, and the blueness of the nail is not local, but total.
However, the presence of blue spots can be explained quite simply. Perhaps you used a dark varnish without using a protective base. The nail may not be completely painted, for example, if the varnish was applied after polishing. Dark color will appear in those areas where cutting took place most intensively.
[yandex3] [google3]
About treatment
How to treat hemorrhages on the nail plate of the thumb? If the leg is damaged and the hematoma covers the entire nail area, the entire hematoma is treated, and not just the damaged nail. At the moment when the finger was injured, cold is applied to it through the tissue surface.
The duration of such exposure should not exceed 20 minutes, then a pause is necessary. This manipulation will reduce pain and the area of the hematoma.
The doctor prescribes medications to relieve pain.
You can apply gels locally to relieve pain. After a few days, an ointment containing a heparin component is used. Non-traditional methods of treatment can also complement basic treatment measures, which should be used after consulting with a doctor.
Dynamics of development
A subungual hematoma usually does not appear immediately after an impact. Swelling and redness of the finger may appear, but a hematoma will form only after a couple of hours. During this time, blood from the burst vessels will not only have time to escape, but also accumulate under the plate. After approximately the same period of time, swelling and bruising on the finger occurs, although it may be much faster. The hematoma then appears last.
At first it only appears as a small pink spot, which then causes the nail bed to change color from pink to crimson. Then the nail begins to turn blue, which is accompanied by a feeling of numbness and pain. After this, a fairly large purple spot is formed. The pain begins to gradually decrease and may disappear completely. However, with severe injuries it usually still persists.
After several days, the spot begins to actively darken. It turns from purple to dark blue. Over time, the edges become even sharper, and the area of the dark spot decreases. Then it continues to decrease. By this time, the pain disappears completely or is present only with pressure.
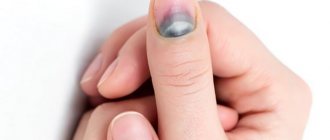
By the time about a week has passed after the injury, the hematoma becomes black and about three to five millimeters in diameter. At the same time, its edges are clearly defined and there is no pain. After this, within about another week, it may completely resolve and disappear.
However, most often this does not happen and the hematoma remains on the plate. Although initially it was an accumulation of blood under the nail, during its development the blood is absorbed into the plate and stains it. Therefore, most often, the hematoma does not disappear anywhere and is located on the plate in the form of a black dot or spot. It can be masked by covering your nails with dark varnish, as this will not harm anyone. As the nail plate grows, the hematoma will move towards the free edge and as a result you will be able to cut it off completely.
Polishing will not help you get rid of a bruise. It is located on the side of the plate that is adjacent to the bed, and therefore only regrowth can rid you of it. By the time the spot is completely localized, it is no longer painful at all.
[yandex2] [google2]
https://youtu.be/H6DAWaaLXsw
?list=PLHapwth4SA4s9HEs-S2gIFMQCSrW3va-t
How does a hematoma appear under the nail?
Why did the bruise appear under the nail plate? When an impact occurs, blood accumulates under the nail plate from damaged vascular tissues. This blood does not flow beyond the nail area because it is too dense, so the blood is trapped under the nail. Blood clotting occurs, after a certain period its color changes until it is completely absorbed.
A few minutes after a person is injured, the nail area becomes red, after a certain period it turns blue. When the blood has clotted, the nail plate will turn black.
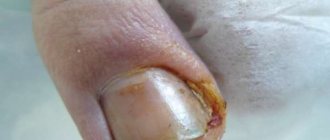
The process of resorption of the blood clot is long, the nail slips and is replaced by a new nail plate. Accumulated hemorrhage under a burst nail, if the injury is not treated, is the cause of the addition of an infectious process, which will lead to the destruction of tissue structures.
The soles of the feet and hands with nail plates become covered with black spotted formations due to mycoses and skin melanoma. They are similar to hemorrhages, but as the nails grow, they do not disappear, but destroy the nail plate.
Consequences
A bruise under the nail can be treated quickly and easily, but if the patient decides to ignore this problem, he will have to face complications. The fact is that due to the hematoma, a void forms between the nail bed and the cornea. And any infection or bacteria can easily get there. It should also be noted that the dead part will remain on the finger until the plate is completely renewed. However, the newly growing nail is quite fragile in composition, which predetermines its inevitable deformation if the patient wears uncomfortable, constricting shoes. Such things should be avoided.
Subungual melanoma
Nail melanoma
One of the varieties of ordinary melanoma is its subungual appearance. A characteristic sign of the neoplasm in question is darkening of the skin around the nail bed. Later, a tumor appears, which destroys the nail. As the disease develops, not only swelling and bruising appear, but also sanguineous fluid and pus. This process will cause too noticeable discomfort and pain, so it is better to consult a doctor immediately.
At the initial stage, it is quite difficult to diagnose melanoma, because it is very similar to a regular bruise. But, if a person is absolutely sure that he did not hit himself anywhere, then he should consult a doctor immediately.
To determine melanoma, you need to do a biopsy, which can accurately confirm the diagnosis and set a time frame for removal of the lesion.