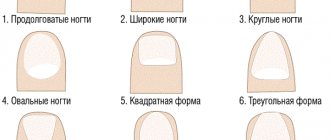
Causes of growths under toenails
Most often, growths appear on the big toe. They occur due to wearing tight, uncomfortable shoes. Pressure forms inside, which disrupts the normal nutrition of tissues. As a result, dystrophic changes appear and an ingrown nail is formed. At risk are women who wear high heels and older people who are overweight.
A growth on the leg can form due to a splinter, glass shard or other foreign object getting under the nail plate. When a finger is injured, the nail breaks down and peels off, and the inner pocket fills with dirt and dead horn cells.
Infection often occurs in such a situation. In the absence of hygiene and high sweating, favorable conditions arise for the proliferation of fungi and pathogenic bacteria. Their vital activity leads to the development of destructive processes, which cause the formation of white growths.
Another provoking factor is cutting off the overgrown edge with dull scissors. It causes inflammation, which stimulates the formation of flesh-colored growths.
Other causes of this disease include:
- wearing dirty socks or wet shoes for a long time,
- disruptions in the endocrine system,
- weakening of the immune system,
- psychological disorders and stress.
The presence of several provoking factors at once increases the risk of skin defects under the toenails.
Myth 2: It’s easy to recognize nail psoriasis by its symptoms.
Actually not always. The fact is that
The nail can react to various diseases with only a limited number of symptoms. Therefore, the manifestations of various diseases on the nails may look the same.
Of course, nail psoriasis can be suspected if the patient has severe symptoms of vulgar psoriasis. However, the damage to the nails may be minor compared to the manifestations of the disease on the skin, and the doctor can easily ignore them.
Usually, the more active the psoriasis is on the skin, the more severe the damage to the nails.
The first to be affected are the fingernails.
And it is also important to know that in 5% of cases, nails may be the only initial manifestation of psoriasis. That is, the classic manifestations of psoriasis on the skin may be completely absent.
What nail psoriasis looks like depends on where the pathological changes originate - in the matrix or the nail bed.
The source of symptoms - matrix or bed - is important to consider when choosing treatment. Therefore, it is necessary to define it correctly.
Manifestation of psoriasis symptoms on the nails
Symptoms that originate in the nail matrix are:
- thimble symptom,
- white spots and dots (leukonychia),
- red dots on the hole,
- crumbling nails.
Although the cause of these symptoms is at the matrix level, as the nail grows, pathological changes appear on the nail plate.
Symptoms that are caused by the nail bed are:
- nail detachment (onycholysis),
- longitudinal hemorrhages,
- subungual hyperkeratosis,
- oil stain symptom.
Next, we will dwell in detail on each symptom separately. And let's start with the manifestations that originate in the matrix.
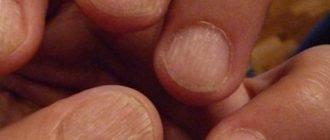
Thimble symptom
The thimble symptom manifests itself on the surface of the nail plate as holes or pits that are similar to the indentations of a thimble.
Such defects occur mainly on the fingernails, but they rarely appear on the toes. As the nail grows, the pits move from the nail fold to the edge of the nail plate.
The pits in nail psoriasis are usually deep, large and randomly located. They arise due to the desquamation from the surface of the nail of loose accumulations of cells in which division and keratinization are impaired.
Thimble symptom - multiple depressions on the surface of the nail plate
The more severe the psoriasis, the more often the thimble symptom occurs.
However, it should be taken into account that in addition to psoriasis, pits on the nails are also characteristic of focal alopecia (baldness), eczema, dermatitis, and can also occur, for example, with a fungal infection.
Counting the total number of pits on all nails will help make the correct diagnosis.
- Less than 20 is not typical for psoriasis,
- from 20 to 60 - psoriasis can be suspected,
- more than 60 - confirm the diagnosis of psoriasis.
White spots (leukonychia)
Leukonychia is a symptom that appears as white spots or dots on the nails.
Psoriatic leukonychia appears as smooth white dots
With leukonychia (from the Greek leukós - white and onychos - nail), in contrast to the superficial pits with the thimble symptom, cells with impaired division and keratinization are located in the thickness of the nail plate. The surface of the nail remains smooth. And the white color of the spots occurs due to the reflection of light from clusters of loosely located cells.
However, some studies suggest that leukonychia is so common in healthy people that it is not a hallmark symptom of psoriasis. For example, the cause of leukonychia can be an injury during a manicure.
Crumbling nails
When superficial pits (thimble symptom) and deep zones of leukonychia (white spots) merge, the nails begin to crumble.
Nails crumble when areas of leukonychia and pits merge
Typically, nail crumbling occurs with long-standing nail psoriasis.
And the more intense the inflammation of the nail matrix, the more the nail plate is destroyed. In severe cases, the nail may completely break down and fall out.
Red dots on the nail hole
Apparently, red dots in the area of the hole and its general redness occur due to increased blood flow to the vessels under the nail.
Also, red dots on the hole are formed due to a disruption in the structure of the nail plate itself: it becomes more transparent and thinner. And because of this, firstly, the vessels become better visible, and secondly, the thin nail plate puts less pressure on the vessels beneath it, and they become more filled with blood.
Red dots in the area of the nail hole (lunule)
Thinning of the nail plate can also cause the entire nail bed to become red.
Nail detachment (onycholysis)
Now let's look at the symptoms that originate from the nail bed.
Onycholysis is the separation of the nail plate from the bed due to the accumulation of cells under the nail with impaired division and keratinization.
Onycholysis extends from the edge of the nail to the nail fold
Onycholysis itself (from the Greek onychos - nail and λύσις - division) is not necessarily a sign of psoriasis and can develop, for example, as a result of a nail injury.
Initially, the loss of contact between the nail and the bed occurs in the hyponychium zone - along the outer edge of the nail plate. Then onycholysis spreads towards the nail fold in the form of a semicircular line. The peeling area turns white due to the accumulation of air under the nail.
A reddish border (scientifically called erythema) along the edge of onycholysis, which is usually visible on the fingers, is characteristic of psoriasis and helps to make the correct diagnosis.
Onycholysis - separation of the nail from the nail bed; a reddish border (erythema) is visible along the edge of onycholysis.
With prolonged onycholysis, the nail bed loses its properties and the growing new nail will most likely not be able to attach to it normally. Therefore, even with complete renewal of the nail plate, onycholysis often persists.
Due to the fact that onycholysis facilitates the penetration of bacteria and fungi, an infection may occur. This sometimes leads to a change in the color of the nail. For example, a greenish color can occur when the bacteria Pseudomonas aeruginosa (Pseudomonas aeruginosa) and others are attached.
Dark green coloration of the nail due to infection of the onycholysis area with Pseudomonas aeruginosa (Pseudomonas aeruginosa)
Longitudinal subungual hemorrhages
Longitudinal subungual hemorrhages occur in the nail bed and appear as dark red lines 1-3 mm long.
Increased blood flow and swelling in the area of inflammation of the nail bed lead to rupture of capillaries, which manifests itself in the form of such hemorrhages.
Longitudinal subungual hemorrhages at the edge of the nail
Due to the nature of the blood supply, most hemorrhages occur closer to the free edge of the nail - in the hyponychium zone.
Subungual hyperkeratosis
Subungual hyperkeratosis is a collection of keratinized cells under the outer part of the nail plate.
Subungual hyperkeratosis on the thumb
In psoriasis, subungual hyperkeratosis (from the Greek hyper - excessively and keras - horn) is usually silvery-white in color, but can also be yellow. And when an infection occurs, it can become, for example, greenish or brown.
The more the nail is raised above the nail bed, the higher the activity of the pathological process.
On the fingers, subungual hyperkeratosis usually appears as loose layers under the nail plate. On the feet, these masses are tightly fused to the thickened nail.
Severe subungual hyperkeratosis and psoriatic plaques on the toes
Also, psoriasis with damage to the toenails is characterized by a combination of subungual hyperkeratosis with onycholysis (separation of the nail).
Symptom of an oil stain
The symptom of an oil stain appears under the nail plate in areas of yellow-red (salmon) color.
They appear on the nail bed closer to the nail fold and move toward the edge of the nail as it grows.
Symptom of an oil stain - salmon-colored areas near the area of nail plate separation (onycholysis)
The cause of this symptom is inflammation of the nail bed with dilation of capillaries and accumulation of cells involved in inflammation, as well as cells with impaired division and keratinization.
Oil stains can come in different shapes and sizes. They can occur both in the center of the nail and on the edge, near the area of onycholysis.
Types of growths
Normally, human nails are horny plates of a pale pink color. They have shine and a smooth surface. The appearance of thickenings, deformations, stripes and growths indicates the development of pathology. To facilitate the process of identifying and identifying the disease, doctors divide such defects into two groups: subungual and periungual growths.
Rough and hard formations of a round shape, grayish in color with dark dots inside may form under the nail. Any characteristic indirectly indicates the reason for their formation.
Factors indicating the development of a fungal infection:
- inflammation of the skin around the thumb,
- plate delamination,
- change in nail color,
- the appearance of severe itching, intensifying at night.
Factors indicating an ingrown toenail:
- delamination,
- purulent boils,
- changing the shape of the plate,
- severe pain around the cushion.
With psoriasis, the nails begin to turn yellow and decay, and flesh-colored growths appear underneath them.
The growth of rough warts localized under the nails of the little fingers is evidence of infection by the human papillomavirus.
If any pathology is detected, you must consult a dermatologist. Based on an external examination, he will make a preliminary diagnosis and, to confirm it, will take a scraping from the affected area and send the biological material for microscopy. After deciphering the tests, the doctor will confirm or deny the nature of the disease, identify the pathogen and draw up the correct treatment regimen.
Skin growing under the nail
Modification of the nail plate
Toenail diseases develop at different ages. Brittle and thick, uneven and curved, colorless and layered nails are all signs of disease. Sometimes diseased nails fall off, after which new ones do not grow for a long time. As you age, these problems can become even more common as circulation deteriorates due to aging.
The most common diseases of toenails:
- dyschromia, which manifests itself as a change in nail color;
- fungal diseases and bacterial infections;
- thickening and rejection of the nail plate;
- delamination;
- nail injury;
- ingrown nails into the skin.
Nail diseases arise from negative effects on the keratin that makes up the nail plate. The condition of the nails is negatively affected by infections, acids, alkalis and various external factors that cause their diseases.
Problems with toenails occur for various reasons. When a person walks, his legs are constantly under tension. Tight shoes often injure your fingers and cause your nails to become deformed. When visiting a bathhouse or swimming pool, the nail may become infected with a fungal infection. Chemicals found in varnishes and soaps can cause nail splitting.
Fungal infections
Yellow nails are evidence of fungus
The nail affected by the fungus weakens, may crack or become rough, change color (as in the photo), flake or crumble. Irregularities or growths appear on the surface.
Fungal infections cause fluid to accumulate under the nail plate; a bruise may appear on its surface, and the nail itself becomes deformed and becomes an unnatural color. This happens especially often with the plate of the big toe. The fungus very quickly spreads from damaged areas to healthy areas and neighboring fingers.
Fungal infections can affect the nails due to improper foot care. People who regularly use saunas, swimming pools and other crowded establishments can become infected with the fungus. Factors that increase the risk of developing fungus also include flat feet, poor-quality shoes, increased sweating of the feet, and diaper rash.
At an early stage, foot fungus is treated with external agents with antimycotic properties that act on the pathogen at its location. These products are available in the form of a spray, gel, ointment or varnish and provide the desired effect only for minor manifestations of fungal infections.
Advanced fungal infections that have affected more than half of the nail or several nails cannot be cured with external ointments alone. In this case, their complex treatment is used, which consists of medicinal ointments and tablets.
Reasons for appearance
The main causes of nail growths are lack of hygiene or injury.
- dirty gray color;
- hard and rough;
- has an oval or round shape;
- There are black dots inside.
A painful growth on the nail plates can appear when a foreign object (a splinter, a piece of glass) gets under the skin or when a finger is injured, when the nail peels off and is destroyed. White growths under the nails are evidence of fungal infections.
Cutting nails with dull scissors promotes the appearance of an inflammatory process, which may result in the formation of flesh-colored growths on the fingers.
The causes of this disease can also include:
- long-term wearing of dirty, damp or wet shoes;
- wearing narrow and uncomfortable shoes;
- the presence of ingrown nails, calluses in the periungual area;
- increased sweating of the feet, skin diseases;
- failure of the endocrine system;
- weakened immune system due to the presence of HPV;
- nervous stress, psychological disorders.
Ingrown nail
Inflammation on the finger due to an ingrown toenail
Another common foot disease is an ingrown toenail. Ingrowth occurs when it is trimmed incorrectly and untimely. When people cut the corners of their nails, they leave sharp ends that can dig into the skin and create small wounds. Infection easily penetrates these areas.
Ingrown toenails most often occur on the big toe. Ingrowth should be treated using several methods:
- Shoes should be comfortable and wide, without heels, and tailored to the size of your feet. Pointed-toe and square shoes contribute to finger rubbing and ingrown toenails. Feet should take a break from shoes as often as possible.
- Foot care should be timely and correct. Be sure to regularly wash your feet in warm water. You should choose simple soap, without harmful dyes that can cause allergies.
- It is necessary to make foot baths with the addition of soothing medicinal herbs.
Sea salt relieves inflammation and redness well. The affected area should be washed with a disinfectant solution of potassium permanganate or furatsilin. The ingrown area should be wiped with hydrogen peroxide. It is imperative to show the problem to a dermatologist. The doctor will prescribe medications to facilitate the healing process or, in severe cases, refer you to a surgeon.
Features of treatment
After identifying the root cause of the growth on the nails, appropriate therapy is prescribed.
The appearance of growths on the nails may indicate the presence of such diseases in the human body:
- A fungal disease affects the skin around the nail. The hardened skin is constantly cut off, which leads to its deformation.
- Splitting and detachment of the nail plate, frequent itching, and purulent abscesses are signs of an ingrown nail. This disease is typical for toenails.
- Psoriasis deforms the nails on the fingers. They begin to turn yellow and collapse, and small bodily growths appear.
- HPV causes the growth of small, rough warts located under the nails of the little toe or near other toes.
If any growths are detected, you should consult a dermatologist who will conduct an external examination and take a laboratory scraping of the affected area, which will help determine the method of dealing with the growth. If severe purulent inflammation appears, you need to see a surgeon. He will carefully open and clean the wound with disinfectants.
Hematoma formation
Bruise under the thumbnail
Nail diseases also develop due to mechanical damage to the fingers. Injury can be caused by a blow from a heavy object, resulting in bleeding and hematoma formation. The nail takes on a blue tint, which indicates burst blood vessels. A slight hematoma, or simply a bruise, quickly resolves on its own.
If the nail is swollen, the area around it is red and very painful, medical attention is needed. You will also need the help of a doctor if, after an injury, the nail begins to peel or purulent discharge is observed from under the nail plate. If the peeling is complete, the nail will need to be removed.
Nail dystrophy, which occurs when it is injured, provokes the development of dyschromia. It radically changes its color, becoming almost black. Dystrophy causes a feeling of rejection of the nail; it begins to gradually atrophy.
Injury to the nail plate and subsequent dystrophy can also manifest itself in excessive flexibility of the nail. Lump-shaped growths often form on the damaged area of the nail plate.
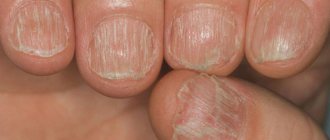
Nail splitting
Dehiscence of the nail plate
A popular reason for nail splitting is a lack of vitamins and nutrients necessary for its nutrition. People who follow a strict diet may be the first to encounter the problem of dissection.
You can protect yourself from this disease with a balanced diet. The diet must contain a sufficient amount of protein, which is used by the body to build cells.
Therefore, it is necessary to eat fish, chicken, and eggs.
Brittleness and weakening of the nail plate is caused by a lack of magnesium in the body. It can be obtained from seaweed, mustard, buckwheat porridge, oatmeal and nuts. Magnesium promotes rapid cell growth. Another essential element for nails is calcium. Its reserves can be replenished by consuming dairy products, as well as beans, peas and garlic.
Features of treatment of growths under the nails
At the initial stages of development, pathology is treated conservatively. The patient is prescribed creams and ointments for topical use, tablet preparations, and vitamin and mineral complexes.
Medicinal methods of combating growths on nails
To speed up the natural process of renewal of the nail plate and destroy the infection, ointments with an antibacterial or antimicrobial effect (Clori) are prescribed and systemic antibiotics or antimycotics are prescribed.
When warts grow on the foot under the toes, ointments (Isoprinosil) and tablets with an antiviral effect (Oxolin) are used.
If there is an inflammatory process and cracks appear, doctors recommend using Vartek ointment. It promotes rapid healing of wounds.
If there is severe pain in the finger, Vishnevsky ointment and an alcohol compress will help get rid of it.
Alternative medicine can be used to enhance the therapeutic effect.
Folk remedies
Effectively help get rid of the defect:
- Compresses with gruel made from fresh onions.
- Applications with ointment made from butter and garlic pulp.
- Applying a flat cake, the dough of which was mixed from flour and 9% vinegar.
- Lotions with pure celandine juice.
Before using traditional medicine, you must first do an allergy test.
Treatment of fungus under the fingernail
Treatment of onychomycosis on the hands requires an integrated approach. The optimal treatment method is a combination of external and systemic drugs with folk remedies. During therapy, it is necessary to exclude the consumption of flour, sweet foods and alcoholic beverages from the diet. The daily menu should include proteins, vegetable fiber, vitamins A, C, E.
The criterion for correctly chosen treatment is the disappearance of symptoms of a fungal infection, complete regrowth of a healthy nail, three times negative tests for fungi (immediately after the course of therapy, after 2 and 4 months). A prerequisite for getting rid of onychomycosis of the hands is disinfection of bed linen, household items, and common areas.
If fungus appears under your extended nails, you need to remove them and consult a dermatologist. After diagnosing and identifying the type of fungus, the specialist will recommend an antifungal agent in the form of an ointment, gel, or varnish. If the disease is complicated, then additional systemic medications are prescribed - tablets, injections. If treatment is ineffective, the doctor may refer you to a nail plate removal procedure.
Remedies for fingernail fungus
Finding out what the most effective medicine for fingernail fungus is today is very difficult, because the pharmaceutical industry offers a huge selection of antifungal agents. Only a specialist can decide which methods and treatment regimens will be the most effective for a particular person. Antifungal drugs for onychomycosis on the hands are prescribed taking into account certain rules:
- an accurate diagnosis can only be established by a dermatologist;
- to prevent the development of side effects during the period of taking antifungal drugs, all others should be abandoned;
- the course of treatment with systemic drugs against the fungus must have a certain duration to achieve stable recovery without relapse of the disease;
- Doctor examinations are carried out at the beginning of treatment 2 times a month, then once.
Antifungal agents include tablets, injections, broad-spectrum external varnishes, ointments, gels, sprays, and special patches. If the infection spreads to the skin around the nail, creams that have a fungicidal effect (Loceril, Atifin) may be recommended. In the later stages of onychomycosis, surgical treatment is prescribed.
- How to remove wrinkles above the upper lip - products and procedures for women
- Fish in Polish - recipes with photos. How to cook cod or pollock in Polish sauce with eggs
- Diet oatmeal cookies
Oral antifungal medications
To avoid rapid destruction of the nail plate, doctors, along with antifungal creams and ointments, prescribe antimycotics for internal use. When taking oral drugs of this group, it is necessary to strictly adhere to the regimen and treatment regimen. You cannot stop the prescribed course yourself, change or skip the prescribed dosage. The most effective oral drugs for onychomycosis:
- Nystatin. Antifungal drug from the group of polyenes. The drug is active against yeast-like fungi Candida albicans. Take Nystatin regardless of meals up to 6,000,000 units/day. Children over 1 year of age are prescribed tablets at a dose of 250,000 units 3 times a day. Duration of treatment is from 10 to 14 days. After a week, the course can be repeated if necessary. The drug is not prescribed for pancreatitis, liver pathologies, ulcers, or during pregnancy.
- Ketoconazole. Antifungal agent of the azole group. The drug is active against dermatophytes, yeast-like, higher and dimorphic fungi. Take for children and adults weighing more than 30 kg from 200 to 400 mg/day 1 time with meals. The average duration of the course is 2 weeks. Contraindications to taking the drug: age under 3 years, pregnancy, liver disease, hypersensitivity to components.
Ointment
The effectiveness of external antimycotics is determined no earlier than 2 weeks from the start of treatment. Local drugs are divided into two groups: azole and allylamine. Among them the most popular:
- Terbinafine. Antifungal ointment of the allylamine group. Active against almost all fungi that cause onychomycosis on the hands. Before using the ointment, you need to remove the keratinized areas of the affected nail with a file, and cut off the overgrown plate with scissors. Apply the drug in a thin layer to the area affected by the fungus. When spreading, it is recommended to include healthy adjacent areas of the skin for prevention. Afterwards, you need to wait for the ointment to dry and apply a bandage. You need to use the product 1-2 times a day for 4-6 months.
- Clotrimazole. Antimycotic of the azole group. Active against molds, yeast-like fungi and dermatophytes. For fungus under the nails, after hygiene of the nail plate, apply a thin layer 3-4 times a day, then rub in gently. The treated area is not covered with a bandage. The fungus should be treated with ointment until recovery and for 2 weeks after symptoms disappear for preventive purposes. Contraindications to the use of the drug: first trimester of pregnancy, hypersensitivity to the active substance.
Antifungal nail polishes
For local treatment of the nail plate, antifungal varnishes are considered the best, since they, unlike ointments and gels, do not wear off. The preparations are liquid, so they are applied to the nail, after which it dries quickly. The varnish easily penetrates the structure of the plate, filling even microcracks. Fungus pathogens under the nail begin to die within 48 hours after applying this product. The best varnishes against onychomycosis on hands:
- Oflomelid. Active against all types of fungi at the initial stage and even in advanced forms of the infectious process. The product must be applied 1-2 times/week until complete recovery. Do not use varnish during pregnancy or while breastfeeding.
- Batrafen. Effective in treating 58 types of microorganisms that cause nail fungus. Varnish therapy is designed for 3 months. Application schedule: 1 month – every other day, 2 months – 2 times/week, 3 months – 1 time/week. The duration of therapy is from six months. Contraindications to the use of antifungal varnish are age under 10 years, pregnancy, and lactation.
How to cure fungus on hands surgically
If the prescribed treatment does not help, and the patient constantly experiences pain from the fungus, the doctor will prescribe removal of the damaged nail. There are several methods:
- Hardware pedicure. This is not a cosmetic procedure, so it is performed exclusively in a hospital. A pedicure is performed using a special cone-shaped nozzle with an abrasive coating. The nail is first softened with special means, then removed layer by layer. The procedure is absolutely painless.
- Laser treatment. The laser beam heats the exact site of infection, which destroys the pathogen. Nail removal occurs under local anesthesia and takes several minutes. During the intervention, healthy tissue is not affected. A new nail grows within six months.
- Surgical method. This method is rarely used, since there are more painless methods. The nail is removed with a scalpel after local anesthesia. After surgery, the wound is treated with an antibiotic and bandaged. Healing occurs over several weeks.
Folk remedies
If you detect an infectious process in the nail during the procedure, you can cure the fungus using traditional methods. The advantage of this treatment is that, unlike medications, natural recipes do not have a toxic effect on the body and do not disrupt the functioning of internal organs. Effective folk remedies against nail plate fungus:
- Essential oils. Use herbal extracts against fungus on the hands in the form of baths and compresses. The best oils for treating nails are tea tree oil, rosemary oil and lavender oil. You can directly lubricate the affected nail with them several times a day, drop 10 drops into hot water along with an iodine solution for baths, which should be taken daily for 15 minutes, or mix with water and apply the mixture to a cotton swab, making compresses at night.
- Tea mushroom. The two-month infusion should be boiled for 1 hour, strained, and brought to room temperature. At night, soak a cloth in a solution of kombucha and apply it to the sore nail. The procedure should be repeated until the situation improves.
Prevention methods
You can prevent the appearance of growths on your fingers by adhering to the following rules:
- keep your feet dry and clean,
- do not wear someone else's shoes and buy them, choose a pair in which the big toe and little toe do not experience much pressure when walking,
- take replacement flip-flops or slippers with you when going to public saunas, baths, swimming pools,
- use individual bath accessories,
- immediately treat wounds with antiseptic agents,
- take vitamin-mineral complexes in spring and autumn.
Compliance with these preventive measures will preserve the beauty and health of your toenails.
Hyperkeratosis of toenails and fingernails: how to treat?
Nail Hyperkeratosis
Hyperkeratosis is a type of fungus that appears due to the rapid proliferation of skin cells. The disease on the fingernails and toenails manifests itself as keratinization of the layer of skin under the nail plate. Hyperkeratosis is expressed in an increase in the nail layer, its delamination, changes and deformation of the nail plate.
To treat hyperkeratosis of fingernails and toenails:
- Tablets are used in conjunction with various ointments and gels, as well as medicinal nail polishes - Fluconazole, Ketoconazole, Nizoral .
- Antifungal tablets, where the main active ingredient is group Amphotericin .
- The use of ointments and gels is necessary to relieve itching and reduce the burning sensation - Lamisil, Batrafen, Neilexpert . The cream, penetrating deep into the nail plate, kills the fungus and, nourishing the skin around it, prevents the disease from spreading further.
- To treat the disease, in the initial stages you should use special varnishes that destroy pathogens - Loceryl, Demicten .
- An antifungal spray is used to treat the foot and interdigital space - Mikozan .
Most often, to treat hyperkeratosis, dermatologists prescribe antifungal gels to their patients with the active ingredient Naftifine , which is aimed at improving the effect of tablets and capsules. Only such comprehensive treatment will help and get rid of the fungus.
Advice: The drug Fluconazole helps get rid of the fungus very well. But you need to drink it within six months. Only a doctor should prescribe the dosage. Self-medication is dangerous to health, as this drug can negatively affect liver function.
Naturally, do not forget that it is the complex and the system that are the best that can defeat the disease. Drink the medicine systematically, at certain times of the day, and also use varnishes, sprays and ointments to treat the nail plate.
Allergic hyperkeratosis of nails: symptoms, causes, treatment
Allergic hyperkeratosis of nails
Hyperkeratosis is a series of dermatological diseases in which there is an excessive increase in the stratum corneum of the skin. Fungal infection of the nails causes subungual hyperkeratosis. The nail plate begins to thicken, which brings a lot of inconvenience, pain and discomfort.
The main causes of allergic hyperkeratosis of the nails include:
- Dysfunction of the immune system.
- Complication from psoriasis.
- Severe stress
- Chronic eczema
- Intestinal tract disorder
- Excess of vitamins
- Diabetes
- Acute viral infections
Important to know: For effective treatment, it is important to diagnose this type of hyperkeratosis in time and make the correct diagnosis. Therefore, if you have any health problems, consult a doctor.
The main symptoms of allergic hyperkeratosis:
- Weakening of the nail plate
- Changing nail color
- Plate delamination
- Nail deformation
- Sealing of the nail plate
Treatment of allergic hyperkeratosis must begin immediately, because over time the disease will progress and can spread throughout the body. When the diagnosis is made, the doctor prescribes:
- Complex treatment using various antifungal drugs, both for external use (sprays, ointments, varnishes) and internal (tablets). See above for a description of what medications can be used to treat this disease.
- Antihistamines are prescribed for allergies Zodak, Dezal, Suprastinex and so on.
As mentioned above, it is necessary to take medications until a healthy nail grows. The standard course of treatment for subungual hyperkeratosis is from two to six months.