When is nail plate removal indicated?
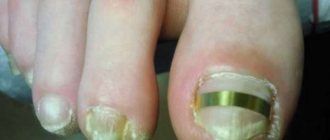
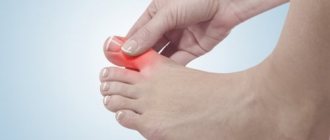
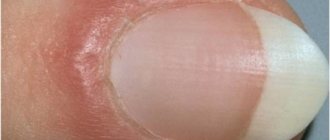
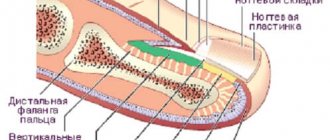
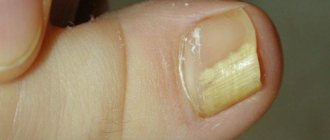
You need to know that an ingrown nail into a big or other toe is not just an unpleasant external defect, but a disease called onychocryptosis. With this disease, the sharp edge of the nail plate grows and digs into the periungual fold. Because of this, the soft tissues of the finger become inflamed, suppuration may occur, and it becomes painful for the person to walk. The main reasons for ingrowth can be:
- wearing narrow, tight shoes that put too much pressure on your toes;
- incorrect pedicure, in which the edges are cut too deeply;
- fungal diseases;
- injury.
Home treatment for onychocryptosis of the thumb can be carried out only in its initial stages, provided that the nail is not deeply ingrown and there is no suppuration. In such cases, you can steam your leg and try to pull out the ingrown edge yourself. If the disease is already advanced, then the patient is advised to remove the ingrown toenail by surgical or other method.
For fungus
This procedure for mycosis of the nail plate of the big toe is prescribed in cases where conservative methods of treatment at home (ointments, special varnishes, etc.) have not solved the problem. The doctor performs removal if there is a risk that the fungus will quickly spread and affect healthy nails. During this manipulation, the doctor removes cells damaged by mycosis and thoroughly disinfects the exposed skin to get rid of microorganisms. Later, a healthy nail plate will grow on this finger.
Removing an ingrown toenail
Such manipulation cannot be avoided if the edge of the plate is deeply embedded in the periungual ridge of the thumb. At this stage, a person is no longer helped by foot baths, treating the affected area with antiseptics and cutting the nail independently - it continues to grow deeper into the skin. In addition to severe pain, this process may be accompanied by puncture of the soft tissues of the finger until they bleed and become suppurated. If such changes appear, you should immediately consult a doctor, who will assess the degree of progression of the disease and perform partial or complete excision of the nail plate.
What not to do if you have a fungal infection
Onychomycosis actively develops in conditions of high humidity, heat, poor lighting and stale air. These conditions correspond to some public places, visiting which requires compliance with certain rules.
To avoid infection it is recommended:
- use the services of nail salons with a good reputation;
- visit saunas and baths in which sanitary and hygienic standards are observed;
- wear your own shoes in swimming pools and gyms;
- When you return home, apply an antifungal agent.
Washing your feet daily, changing your socks and hosiery, and ironing your bed linen will help prevent infection.
At the first signs of infection, treatment begins immediately. Follow the doctor’s recommendations and prescriptions until you are completely free of pathological microorganisms. If you stop using medications at the first signs of recovery, the infection will return again and spread to neighboring areas.
The development of a mycotic infection cannot be allowed to progress to such an extent that radical measures are required.
How to remove a toenail
When the doctor says “resection of the nail plate is necessary,” most people get goosebumps, because they immediately imagine a clinic office, surgical instruments, a wound, blood, pain. You shouldn’t delve into such thoughts, because in reality, enduring pain every day with every step is much more painful than having your big toenail removed for medical reasons.
You also need to know that today other methods of treating onychocryptosis are used - for example, laser removal of a toenail or getting rid of the disease using radio waves. A person who suffers from this disease simply needs to compare the different ways in which the thumb can be cured. The patient can make a balanced choice of treatment method by comparing which treatment method is most suitable for him:
- by type of impact;
- healing rate after intervention;
- price for performing the manipulation;
- the amount of necessary medications.
- Potatoes baked in the oven: recipes
- Causes of diabetes mellitus
- Herbs for weight loss that burn fat in the pharmacy. Collections of fat-burning herbs and reviews of those who have lost weight
Laser
This is a gentler method of treating onychocryptosis than conventional surgery. Laser removal of an ingrown toenail involves evaporating the overgrown edge by applying high temperature. This procedure is performed on an outpatient basis under local anesthesia and takes up to 20 minutes. After completion, the patient has virtually no painful sensations, because the laser does not affect healthy tissue. This almost halves the patient’s recovery period after the intervention compared to surgery, and also prevents the risk of improper growth of the nail plate in the future.
Operation
This method has been used for a very long time; photographs of this procedure and its results are very common. How to surgically remove an ingrown toenail:
- Under local anesthesia, the surgeon makes an incision in the skin of the big toe over the affected area.
- The ingrown segment is eliminated with a scalpel and part of the matrix of the horny plate is excised to prevent the possibility of ingrowth in the future.
- The wound is treated with antibiotics.
- The patient needs to bandage the next two weeks, apply prescribed ointments to the finger and follow a gentle regime for the leg. Recovery is expected in a month.
Patch
The plaster has become the least traumatic and at the same time affordable. The remedy is often used in home treatment to get rid of fungus-affected toenails of the big toe. Keratolytic patch is a representative of a special group of products; it can be purchased inexpensively in an online store from a catalog. How to remove a toenail using it:
- First, be sure to cover the healthy skin of the big toe with a regular plaster - this will protect it from the effects of keratolite.
- Next, the plaster mass is applied in a thick layer and sealed, leaving it to act for 2-3 days.
- After removing the patch, parts of the affected nail plate are removed with scissors or forceps and the bed is treated with antifungal agents.
- Applications are repeated until complete healing.
Methods of surgical treatment of ingrown toenails
The very presence of an ingrown nail is considered an indication for surgical removal of an ingrown nail, especially if it is accompanied by purulent inflammation, severe pain and deformation. In case of severe inflammation, the surgeon may delay the operation and prescribe anti-inflammatory conservative treatment to reduce the possibility of relapse and complications.
Surgical removal of an ingrown toenail is the most radical method of treatment, but it is not without its drawbacks, the main one of which is the high frequency of relapses. Individual features of the structure of the nail bed, errors in the surgical technique, and non-compliance with the doctor’s recommendations during the rehabilitation period lead to recurrence of the disease.
The essence of surgical treatment, regardless of the chosen technique, comes down to the removal of all or part of the nail with the obligatory destruction of the growth zone. To reduce the rate of recurrence, various modifications of traditional excision of the nail plate are proposed.
The operation to excise an ingrown nail involves local anesthesia with solutions of novocaine or lidocaine, which are injected along the lateral surfaces of the finger. During the manipulation, the patient may feel that something is happening to the finger, experiencing anxiety, but there is no need to be afraid - anesthesia reliably protects against pain. To prevent bleeding, a tourniquet is applied to the base of the finger.
To date, more than a dozen methods for removing ingrown toenails have been proposed. Each of them has both advantages and disadvantages, differs in the area of nail resection, the type of treatment of its bed, and the course of the postoperative period.
The method of simple removal of the nail plate - Dupuytren's operation - is used quite widely, but one cannot help but point out its low effectiveness: the relapse rate is 90% or more even when only half of the nail is excised.
The essence of the operation is as follows:
- Providing anesthesia for the soft tissues of the finger;
- Cutting the nail plate in half with twisting each half with a clamp;
- Careful removal of granulation tissue in the area of ingrowth.
The nail bed remains untouched after nail extraction, but it is possible to excise the periungual ridges and model the shape of the bed for cosmetic purposes.
after operation
The postoperative period for this type of operation is long – several weeks and even months. During this period, the patient experiences severe pain, is forced to give up walking and wearing ordinary shoes, often performing work duties becomes impossible, and a sick leave is issued.
In addition to the high risk of relapse, Dupuytren's operation has another significant drawback - a cosmetic defect. After regrowth, the newly formed nail will be narrower and denser than the removed one; deformation is characteristic; often the nail resembles animal claws, bringing suffering to the patient regarding the aesthetics of the treatment result.
Currently, surgeons are trying to limit the Dupuytren operation to cases where, in addition to ingrowth, there is a fungal infection of the nail plate, subungual panaritium (purulent inflammation), osteomyelitis of the phalanx of the finger or phlegmon.
The type of surgical treatment for an ingrown toenail, when the nail plate remains in the same place, is the Barlett operation , proposed in the first half of the last century. With this type of intervention, on the ingrowth side, 5-7 mm down from the edge of the nail fold, a longitudinal incision is made through which the underlying tissue is removed to the bone. The skin incision is sutured with a silk suture, the tension of the threads of which moves the roller away from the edge of the nail where the ingrowth has occurred. Some surgeons suggested not suturing the tissue, but leaving the defect gaping.
The recurrence rate for Barlett's surgery is about 30%. It is more advisable to carry it out when the inflammatory process subsides somewhat under the influence of conservative therapy.
In 2004, a method was developed for surgical removal of an ingrown nail, when its bed expands, tissue compression in the area of the ridge is eliminated, and the growth zone remains untouched. The method is quite effective, relapses occur in approximately 11%.
The Meleshevich operation, proposed back in 1985, was quite progressive, which involves:
- Resection of the trapezoidal area of the periungual fold;
- Expanding the area of the nail bed;
- Plastic surgery of surrounding tissues.
In a clinic setting, different types of interventions and their modifications are used. Maybe:
- Complete removal of the nail with the growth zone and ridges (the most traumatic, poor cosmetic result, relapses are frequent);
- Removal of the edge of the nail and the growth zone with/without the roller section;
- Resection of a nail fragment with a roller and preserving the growth zone.
One of the frequently used types of surgical treatment for ingrown toenails is the Emmert-Schmieden operation, which in its classical form consists of several stages:
- Longitudinal dissection of the nail, retreating up to 5 mm to its center from the site of ingrowth;
- Removing the affected part of the nail by twisting;
- Deepening the incision to the periosteum with removal of a wedge-shaped section of tissue from the cushion area;
- Bringing the edges of the wound closer together and suturing.
The Emmert-Schmieden operation, like other types of interventions, does not guarantee a lasting effect, and the probability of relapse with it reaches 46%.
The most radical method of treating pathology can be considered total removal of the nail with underlying tissues to the periosteum. Such an intervention requires subsequent plastic surgery of the phalanx with one’s own skin or artificial one. Total nail removal is performed only in advanced cases, when it is impossible to use other methods and the disease recurs.
The consequences of total resection are decreased resistance of the finger to mechanical loads, pain when wearing shoes, injury, and deformation of the distal phalanx. Plastic surgeries designed to improve appearance in a third of cases result in necrosis of the transplanted skin, which gives an even worse result in the end.
When all methods of dealing with an ingrown nail do not bring results, and the patient continues to suffer from constant recurrence, it is possible to remove the entire phalanx of the finger. The operation is mutilating and has extremely low aesthetics, although it eliminates the pathology once and for all. This intervention is more of a "desperation" operation.
As you can see, many surgical techniques have been proposed for the treatment of ingrown toenails, and even more have been developed in a variety of modifications, but none of the methods gives a 100% result. This explains the ongoing attempts to find the best option for removing ingrown toenails.
Price for big toe nail removal
How much this procedure will cost depends on how deeply the nail plate has grown, what method of manipulation is chosen and in which clinic the treatment will take place. Patients must calculate the possibilities: they will have to spend a certain amount, because treatment for onychocryptosis is not included in the list of free medical services. Example options:
- The cost of keratolytic patch therapy in the initial stages of the disease is from 300 to 3000 rubles.
- The price of laser removal of an ingrown nail is from 3000 to 8000-9000 rubles.
- You can get rid of the problem surgically for 3000-6000 rubles.
Read about other methods of dealing with such a problem as an ingrown toenail.
Laser removal of nails with fungus
Laser treatment of nail fungus has become an excellent alternative to surgery. Laser equipment is characterized by precise operation, targeting only fungal spores, without damaging tissues and nails. The procedure takes about half an hour. To completely cure the fungus, you will need about 6 procedures at a certain interval. Before removing a nail affected by a fungus using a laser, the doctor will order a urine and blood test, isolation of the causative agent, and an ultrasound. After laser therapy is completed, tests are repeated to ensure successful removal of the fungus.
The day before the procedure, the nails are steamed in a bath with hot water, soda and laundry soap. After this, your nails need to be trimmed short. The laser is contraindicated for pregnant women, breastfeeding women, and children. Also, laser therapy for onychomycosis is not performed for patients with oncology, epilepsy, or diabetes.
Stages of ingrown nails
Quite often, it is the big toe that becomes the target of an ingrown toenail. This is due to the physiological structure of a person.
As for the reasons, it could be a genetic predisposition, various nail deformations, hormonal levels, or improper pedicure, hygiene procedures, or fungus.
Depending on the degree of damage to the area of the finger, three stages of the disease are distinguished:
- the formation of redness, pain, as well as slight swelling, and the ingrown nail rather weakly affects the soft tissues;
- the second stage is already accompanied by infection, as well as purulent inflammation;
- The third stage of onychocryptosis not only combines the previous two, but is also accompanied by tissue granulation, and inflammatory processes become chronic, which leads to long-term treatment.
Osokin Anton Vladimirovich
Surgeon/oncologist (mammologist), coloproctologist
“To prevent this disease, you need to carefully care for your nails. You should not cut them too often and too much, or excessively round them. You definitely need to use a nail file to work on the corners of the nail plate. In addition, it is not recommended to wear shoes that are tapered to the front. Fingers and toes must be protected from bruises.”
Hardware and surgical methods of nail removal
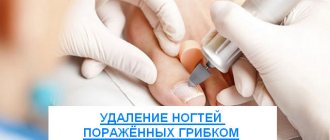
Nail surgery
Surgical removal of the affected area is prescribed for advanced onychomycosis. For this, local anesthesia is used. Patients need to know that dressings are done after surgery (they are also painful).
For the first time after surgical treatment, the patient is advised to remain in bed. Due to severe pain while walking, he lost his ability to work for almost a month.
Important!
Surgical removal of a diseased nail is associated with an increased risk of bacterial infection entering the body. This significantly complicates treatment. A significant disadvantage of surgical removal is the deformation of the newly growing nail plate.
Surgical removal of the nail is a radical way to treat onychomycosis. Due to its danger (there is a risk of infection entering the body), it is rarely used. Much more often, doctors recommend procedures for hardware removal of the plate affected by the fungus.
Hardware pedicure
The procedure is carried out only in a beauty salon. For this purpose, special disinfected pads are used. The essence of this treatment method is that the plate is softened and then cut off layer by layer. This is done to improve the penetration of medicinal drugs into it.
The procedure does not cause any pain. The hardware removal method allows you to quickly get rid of the affected areas. Its advantage is that the duration of treatment with antifungal drugs is significantly reduced.
Laser removal
The essence of this removal method is based on the fact that the nail plate is heated by laser beams, after which it peels off. The laser also allows you to remove the mycelium of the fungus, which eliminates the risk of relapse. Before removal, the nail plate is steamed.
Typically, laser treatment is carried out in several stages. Just three procedures are enough to get rid of the disease forever. Full recovery occurs within 3 to 6 months.
Laser treatment is a promising direction in removing fungus. Patients need to know that it is contraindicated in the presence of the following diseases and conditions:
- Oncological pathologies,
- Diabetes,
- Disorders of blood clotting processes,
- Pregnancy.