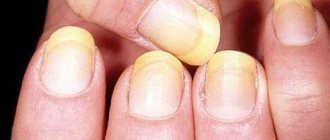
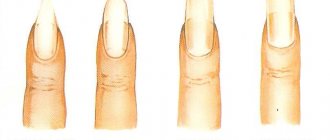
Nail structure
- The nail plates are protected on all sides by rollers . Their posterior layer is called proximal. It binds to the surface of the finger with a thin skin - the cuticle. It brings the young nail to the surface and is no longer needed after that. It is usually removed during a manicure or pedicure.
- There is a bed under the plate. It is richly supplied with blood vessels. In this zone passes the matrix tissue of the nail plate, which extends here from the cuticle zone and has a much smaller layer. Because of this, the nail grows faster on the inner surface in contact with the bed, and on its outer part the cell growth rate is slower.
- Part of the matrix zone of the plate is represented by cells that synthesize keratin . That is why, when this area is injured, further growth of the nail stops and only the skin will remain on the finger.
Causes
Most often, damage to the nail plate occurs due to accidents and unforeseen situations. The reasons are the following:
- fingers getting pinched by the door;
- if a heavy object fell on your hand and pressed the nail plate;
- improperly performed manicure;
- long-term wearing of shoes that cause discomfort in the form of compression (if the toenail is damaged).
Whatever the reason, you need to take the necessary measures as soon as possible to restore the normal condition of the nail.
Important : no matter what causes damage to the nail plate, photos of the consequences of which are very picturesque, it is necessary to restore, treat and strengthen the nail structure, since any wound surface is an opportunity for the development of infection.
Types of injuries
Nail trauma is mechanical damage caused by compression, blows or exposure to sharp or cutting objects, inflammation of the cuticle area, infection with bacteria or fungi.
Nail injuries include:
- bruised nail;
- cuts;
- punctures;
- compression;
- tear due to nail detachment;
- destruction or deformation of the nail due to fungal infection.
Depending on the nature of the manifestations, injuries are divided into acute and chronic. A separate group includes matrix injuries and damage during manicure and pedicure.
Acute trauma
Acute injury is damage that is provoked by intense short-term exposure to one or another traumatic factor (for example, bruise, pinching, puncture, cut or tear of a plate, injury at work, during a manicure or pedicure, etc.). With acute injuries to the nail plates, damage to the integrity of the blood vessels almost always occurs, leading to the appearance of a hematoma under the nail.
For such damage:
- accumulation of blood causes throbbing pain;
- the nail plate first turns blue and then turns black;
- local skin temperature increases;
- the finger swells and turns red;
- in case of severe damage, bruising leads to its further detachment from the bed.
During an acute injury, the plate may be partially or completely torn off. With such bruises, the blood flows out and the pain is less pronounced. However, with such injuries, the risk of infectious complications and the development of suppuration significantly increases, leading to an increase in temperature and the appearance of signs of general intoxication.
Acute injuries may be accompanied by other symptoms:
- puncture of the plate with bleeding;
- tears;
- lacerated wounds with smooth and uneven edges.
When the patient's fingers are fractured or crushed, the motor function of the hand is impaired and intense pain develops.
Chronic injuries
Chronic injuries are those caused by mild, repeated or prolonged exposure to:
- wearing uncomfortable shoes;
- orthopedic problems;
- habit of biting nails;
- getting splinters, splinters or splinters under the nail;
- long-term course of onychomycosis;
- complicated by panaritium, etc.
With chronic injuries, pain, hematoma and swelling are less pronounced due to the absence of severe bleeding. Other symptoms remain the same.
Complications of all chronic injuries are:
- unaesthetic appearance;
- onychodeformation (curvature of the shape and violation of the thickness, transparency and color of the nail plate);
- ingrowth.
Sometimes the process is aggravated by purulent inflammation and fungal infections.
Matrix microtraumas
These injuries are classified into a separate group due to the characteristics of the clinical course. When this area is injured, manifestations occur after some time - usually after 1-2 months, when the nail plate has already grown. Damage to the growth zone leads to the appearance of white spots or dots, transverse convex grooves and other onychodeformations.
Injuries during manicure
These injuries can be either acute or chronic. They occur when the manicure or pedicure procedure is performed incorrectly:
- cuts;
- injections;
- traumatic removal of the eponychium with damage to the matrix.
Injuries leading to infection of the wound around the nail plate are dangerous, since if left untreated, infection can lead to severe purulent inflammation (for example, felon). Also, when using non-sterile instruments in manicure and pedicure salons, there remains a high probability of the client becoming infected with such life-threatening infections as:
- HIV;
- hepatitis B and C;
- syphilis;
- mycoses, etc.
Errors leading to matrix injury lead to various consequences associated with onychodeformation. After such injuries, a person may need a lot of time to correct the unaesthetic curvature of the nail plate.
Classification of bruise by severity
Depending on the severity of the injury, there are several degrees of injury severity:
- mild degree - the nail plate receives minor damage. The pain usually goes away within the first minutes after the injury. The nail may twitch slightly, but no visible changes occur and no hematoma forms;
- moderate severity - soft tissues are slightly damaged, the nail is injured, but the integrity of the plate is preserved. This often happens when a toenail is injured, for example, in children while playing football. The plate may peel off at the edge or receive minor damage on the side. As a rule, in this case, the nail can be cut off, and the damage to the soft tissue can be disinfected and lubricated with brilliant green;
- severe damage is characterized by blueness of the nail plate after injury. Literally before our eyes, the color turns from light pink to dark blue due to the release of a certain amount of blood under the nail. In parallel, the integrity of the nail plate may be compromised beyond the boundaries of contact with soft tissues. Such damage most often occurs during plane impacts;
- very severe damage - pathology occurs with severe mechanical injuries, and according to statistics, damage to the nail on the hand is more common. This could be a hand or fingers getting caught in the mechanism. In this case, the nail receives severe destructive damage, the nail plate can be completely destroyed, and its parts can be pressed into the soft tissue. As a rule, damage is characterized not only by problems with the plate - soft tissue is significantly damaged, open wounds occur, and the finger may be dislocated or broken.
Determining the severity of the injury determines how to treat the patient.
Bruises
The severity of the bruise is determined by the nature of the damage to the soft tissues and the nail plate itself:
- mild – the integrity of the skin and nail is not compromised, the injury is accompanied by fleeting and mild pain;
- moderate severity - a subungual hematoma and swelling appear on the affected finger, the victim experiences severe pain;
- severe - there are bruises on the finger, the integrity of the plate may be compromised, the damaged area swells greatly, the victim suffers from intense pain, there may be a dislocation in the phalangeal area;
- very severe - the nail plate is severely damaged or completely torn off, there is severe swelling, hematomas, severe pain, dislocations, bone cracks and fractures may be detected in the area of injury.
If signs of deformation, severe pain, severe swelling and other manifestations of an inflammatory reaction appear, you should always seek help from a specialist. Voids in the subungual space, untreated inflammation (especially of a purulent nature) and secondary infection of the lesions can lead to dangerous complications and even disability or death from sepsis!
Features of injuries to fingernails and toenails
Particular attention should be paid to ensuring compliance with the rules of antisepsis and asepsis when applying dressings that protect open wounds from infection.
For all types of injuries, it is recommended to make sure that there are no dislocations or fractures: make sure that it is in the correct location and that there are no asymmetries, the ability to move or deviate in one direction or another.
Big toe nail injury
The cause of an acute injury to the big toe nail can be falling heavy objects from a height, being pinched, playing sports, carelessly hitting an object or falling on an uneven surface, being injured in a dangerous workplace, in an accident, etc. Chronic injuries are usually caused by rough pressing on the plate during pedicure, orthopedic pathologies without correction or wearing uncomfortable shoes.
What to do if you are injured?
Acute nail injuries are almost always accompanied by severe pain, which is caused by the large number of nerve endings located at the fingertips. Providing assistance in case of injury always involves not only pain relief, disinfection and dressing, but also a detailed examination of the finger for dislocations, cracks and fractures.
When to see a doctor and which one?
In case of severe trauma, it is necessary to consult a doctor. An immediate visit to the doctor is also necessary if there is any suspicion of a fracture or dislocation of a finger.
It is necessary to contact a doctor if:
- damage to a large area of the nail plate or it has peeled off;
- formation of a large hematoma;
- the finger after the injury is bent and located asymmetrically in relation to the other fingers;
- there is severe pain and swelling;
- there are signs of suppuration;
- there is a limitation in the mobility of the joints of the hand or foot.
When can you treat yourself at home?
You can treat at home for minor injuries with an uncomplicated course:
- absence of large hemorrhage under the nail and swelling of the soft tissues of the finger;
- mild pain that is easily relieved by taking painkillers;
- absence of suppuration.
If you experience an increase in temperature, purulent discharge from under the nail or from wounds, increased pain for three weeks, and impaired finger mobility, you should definitely consult a doctor.
How to give first aid
- Lay the patient down to relieve severe pain and reduce swelling and hematoma. The injured arm or leg should be raised up and a comfortable cushion or pillow placed under it.
- Apply cold to the bruised site for 20 minutes to stop bleeding. Every 10 - 15 minutes, ice or other very cold object should be removed for 10 minutes to prevent frostbite of soft tissues.
- Disinfect the affected nail and existing open wounds with a solution of hydrogen peroxide 3%, chlorhexidine, miramistin. It is necessary to treat the edges of open wounds with Cutasept, iodinol or a 5% alcohol solution of iodine (in the absence of an allergic reaction to iodine). In extreme cases, you can use alcohol.
- In case of severe pain, give the victim to take one of the analgesics (Ketonal, Spazmalgon, Analgin, etc.).
- In case of significant bleeding caused by additional severe injuries, it is recommended to stop it by applying a hemostatic tourniquet or a pressure bandage.
- Apply a sterile gauze pad and, if possible, a pressure bandage to the injured area. It is advisable to immobilize the finger using one or another technique: friendly immobilization (the affected finger is fixed with a bandage to the adjacent healthy one), using splints from improvised means.
Under no circumstances should you try to puncture hematomas yourself. This manipulation can only be performed by a specialist.
If the puncture is performed incorrectly, there is a guaranteed risk of nail rejection and infection! If the nail plate is rejected immediately, the doctor will carefully remove it.
Treatment at home
If the damage is minor and the nail has not turned black, then treatment can be carried out at home. To do this, you must complete the following steps:
- Give the injured finger complete rest for the first time.
- Apply cold compresses to the surface of the plate, replacing them one after another while heating. This will help relieve swelling and reduce pain. If small vessels are damaged, cold will help prevent bleeding. If the pain persists, you can anoint the nail and the surface of the skin around it with menthol ointment - it will create a cooling effect and reduce pain.
- If the soft tissue around the plate is damaged, there are cracks and wounds with minor bleeding, then the surface must be treated with hydrogen peroxide, the finger must be covered with a dry bandage, and if necessary, Levomekol ointment can be applied to prevent suppuration.
- If swelling of soft tissues forms, but in the absence of visible damage, you can draw an iodine grid on the finger - it will help eliminate the swelling.
- If you experience severe discomfort, you can numb your finger by taking a Paracetamol or Ketorol tablet. For a while, the victim will no longer feel pain from the bruise. If the pain is severe, you can apply a compress to your finger, for which Dimexide + Novocaine are mixed in a combination of one to three. Several layers of gauze are soaked generously in the resulting solution and a gauze swab is applied to the nail itself, or the entire finger is wrapped in it. After some time, the pain subsides.
At home, badyaga will help cure an injury. Badyaga, diluted to a dough-like consistency, can be used in the form of applications on the nail plate. After compresses, heparin ointment is used - it will eliminate swelling and help avoid bruising.
An anti-inflammatory effect is provided by an ointment for nail bruises based on the medicinal plant arnica. The product bears the same name - Arnica. You need to lubricate the damaged finger several times a day. Larkspur ointment has a similar effect, which can also be used for damaged fingers.
How does a new nail grow?
In case of severe injuries, the plate is torn away from the bed either immediately or during the first few days. If the matrix has not been damaged, then in the following days the growth of a new nail plate begins. If the growth zone is severely damaged, recovery becomes impossible. In such cases, the victim has to resort to artificial extension (prosthetics) of the plate.
The growth rate of a new nail plate is individual and can be influenced by various factors (hormonal levels, drinking regime, time of year, etc.). In adults, on average, it grows by 0.1 mm per day (or about 4 mm per month), and in the elderly - by 0.0095 mm. Nails grow fastest in children - by 1.5 - 3 mm per day. Moreover, if the matrix has been injured, regrowth occurs more slowly.
Nail plates on the hands grow faster than on the feet. In this case, the plates on the middle fingers grow faster than on the little fingers or thumbs. On average, complete nail renewal occurs in 3–6 months on the hands and 9–12 months on the feet.
How to speed up nail growth after injury
Your doctor may recommend taking the following dietary supplements:
- Pantovigar;
- Merz special dragee;
- Marine calcium with vitamins C and D3 (from Biobalance);
- For hair, skin and nails (from Lady's Formula);
- Zinc (Velmark, Czech Republic);
- Doppelgerz Beauty Biotin et al.
You can try to restore a nail after an injury using the following methods:
- introduction into the diet of foods and dietary supplements high in protein, minerals (sulfur, calcium, zinc) and vitamins;
- refusal to use aggressive detergents;
- procedures to stimulate blood circulation in the nail growth area: massage, home cosmetic baths and masks.
Procedures to restore the nail plates can begin after complete healing of the soft tissues.
The following recipes for home use can be used for baths:
- lemon juice with salt;
- sea salt or soda with iodine;
- gelatin with milk;
- medicinal herbs St. John's wort, chamomile, etc.
The solution should be warm. The duration of the procedure is from 10 to 20 minutes. After completing it, you need to rinse your hands or wash them with soap and lubricate them with nourishing cream. The cuticle area should be massaged. Procedures are performed 2–3 times a week.
Masks to accelerate nail growth can be prepared from different ingredients:
- beeswax and almond oil;
- almond oil with iodine;
- nourishing cream and red pepper;
- cosmetic paraffin.
Masks must be performed 2-3 times a week.
Treatment
The treatment tactics for nail injuries are determined by their clinical picture.
In case of acute injuries, after first aid, surgical procedures can be performed to remove the nail hematoma, part or all of the nail plate. Painkillers are prescribed to relieve pain. After this, the patient is recommended to bandage with various antiseptic and anti-inflammatory agents. It is also necessary to ensure that the affected limb or finger remains at rest during healing. The use of traditional methods of treatment is allowed after consultation with a doctor.
Products and medications for the treatment of acute injuries
- for disinfection : chlorhexidine solution, 3% hydrogen peroxide, miramistin, cutasept, etc.;
- for pain relief and reduction of swelling and inflammation: compresses with Dimexide and Novocaine;
- to reduce bruising , swelling and inflammation: Heparin ointment, Riciniol emulsion;
- for pain relief : Ketonal, Smazmalgon, Sedalgin, etc.;
- to accelerate healing and prevent purulent complications: Levomikol ointment, Sintomycin liniment, etc.;
- to reduce the manifestations of bruises on intact tissues: “Zhivokost”, “Bodyaga”, “Arnica”;
- taking antibiotics (for suppuration).
The frequency of dressings, medications for external and systemic use, and the duration of treatment are determined by the doctor individually.
Surgical methods
If it is impossible to restore a peeled or torn nail without removing the plate, the following types of surgical interventions can be performed:
- removing part or all of the plate using a scalpel;
- removal using radio wave or laser surgery techniques.
If possible, preference should be given to laser or radio wave removal, since these methods help to perform the operation with virtually no blood and accelerate tissue restoration in the postoperative period.
To restore the nail plate, various aesthetic corrective surgeries are performed:
- excision of scar tissue under the nail for better fit (the intervention can be supplemented by implantation of a nail bed graft to replace the defect);
- transplantation of a matrix graft to restore nail growth;
- correction of onychogryphosis with the formation of a new bed, implantation of bone tissue for support and tightening of soft tissues.
Orthonyxia
If it is necessary to eliminate deformations and disturbances in the direction of growth of damaged nails, specialized clinics can perform various methods for non-surgical restoration of nail plates using plates or staples - orthonyxia.
The following special designs are used for this:
- plates: B/S, Onyclip, Podofix, etc.;
- staples: Frazer, COMBIPED, titanium thread, 3-TO, ERKI technology, etc.
According to leading experts, in some clinical cases in which surgery can be avoided, orthonyxia is more effective and the percentage of successful corrections is about 90% (as opposed to 63% of surgical corrections). These techniques relieve the patient of the need for local anesthesia, obtaining sick leave, unpleasant physical sensations and aesthetic discomfort.
Nail prosthetics
If the matrix is severely damaged, plate growth cannot be restored. In such cases, to eliminate the aesthetic defect, prosthetics can be performed using special composite materials.
Possible complications
With severe nail injuries, the following complications may develop:
- rejection of the plate or the need to remove it;
- addition of a fungal infection;
- nail deformation (onycholysis, onychogryphosis, etc.);
- infection and purulent inflammation;
- inflammation of the lymph nodes;
- myositis;
- thrombophlebitis;
- phlegmon of the hand or foot;
- osteomyelitis;
- sepsis;
- general blood poisoning;
- the need for amputation with the development of gangrene.
Some severe complications of nail injuries, accompanied by infection and lack of adequate treatment, can lead to death.
Tips for a manicurist and pedicurist
When clients contact with bruised nails, beauty, manicure and pedicure salons should refer victims to a traumatologist in the following cases:
- severe or extremely severe damage;
- suspicion of a dislocation, crack or fracture of a finger: severe swelling, redness, increased local temperature of soft tissues, pain and limited mobility;
- redness of the skin around the nail plate;
- purulent discharge from the wound;
- increase in body temperature and deterioration in general well-being.
You should be referred to a dermatologist if there are signs of fungal infection:
- change in color, thickness and transparency of the plate;
- itching in the area of injury;
- accumulation of keratinization with an unpleasant odor under the plate in a large volume;
- plate destruction.
Orthonyxia methods for restoring nail plates using special structures can be carried out only after the acute manifestations of injury, purulent or fungal lesions have been eliminated. Manicure and pedicure services for traumatic injuries must be performed after permission from a doctor. Also for such clients, the use of disposable tools and materials is provided: files, grinding devices, applicators for applying medicinal compositions and varnishes, towels.
Folk recipes
As a method of auxiliary therapy for a bruised nail plate, you can also use folk remedies, you just need to coordinate their use with your doctor. The most effective and easily implemented recipes include the following:
- Salt baths help relieve swelling and accelerate healing. To prepare the solution, add a spoonful of salt and soda to a glass of warm water and mix. Immerse the injured finger in the bath and hold until the water cools completely.
- A compress of wine and vinegar helps eliminate pain and restore the nail plate. To prepare it, you need to mix a glass of table vinegar with a glass of wine, add a spoonful of salt, and mix well. Use the resulting solution for medicinal compresses and lotions, preferably before going to bed.
- Bodyaga is an excellent remedy in the fight against bruises. Make a stretchy dough from water and bodyaga powder. Make a small cake out of it and apply it to the injured nail. Leave until completely dry.
- Onion compress. A small onion should be finely chopped, the resulting pulp should be applied to the damaged area, covered with polyethylene, and secured with a bandage or plaster. The optimal exposure time is about half an hour.
A bruised toenail or hand nail is an injury that is accompanied by severe pain and can lead to the development of unwanted complications. Competent first aid, compliance with medical recommendations, the use of ointments, compresses and traditional medicine recipes in combination with restriction of physical activity will give good results and help the nail plate to recover as quickly and fully as possible.
Answers to frequently asked questions
If a nail does not grow back for more than a week, will it recover?
Only a doctor after an examination can make a forecast about the likelihood of the plate growing back.
Is it possible to bandage a torn nail yourself for regrowth?
No. This procedure will not help save the nail plate, and it will not grow. To assess the severity of the injury, you should consult a doctor who, after examining the condition of the matrix, will be able to make an accurate forecast about the likelihood of plate regrowth.
Is it possible to put a hand or foot in cold water after a nail injury?
Yes, but not in all cases. If you have open wounds, it is better to give preference to applying ice or another cold object.
When can you apply polish to a growing nail?
Varnish is an aggressive cosmetic product and it is better to apply it after the plate has been restored, since the substances it contains can slow down the growth of the nail or lead to its deformation.
How to prevent fungal infection when nails are peeling off?
To prevent mycoses, your doctor will select one or another drug for external use. It is usually recommended to use broad-spectrum antifungal agents for these purposes.
Complications and consequences
In some cases, even after careful treatment of the injury site at home, complications arise. The most serious consequences for a finger are if the nail comes off or peels off over time. If there is no suppuration, there is no need to worry in this case - apart from a cosmetic defect, the injury does not threaten the victim with anything. The nail plate will be removed on its own absolutely painlessly, or at the point of origin it will simply grow back to its normal state. You can observe how the light spot will gradually move towards the edge of the nail, and then completely disappear.