Onycholysis of fingernails and toenails: how to treat at home with folk remedies
All iLive content is reviewed by medical experts to ensure it is as accurate and factual as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable sites, academic research institutions and, where possible, proven medical studies. Please note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to such studies.
If you believe that any of our content is inaccurate, out of date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
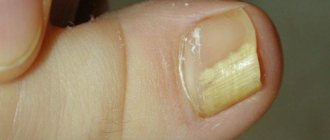
Human nails are very sensitive to various kinds of problems: with a lack of vitamins, they become dull, and with a lack of calcium, they become brittle. It also happens that the nails begin to peel off from their base - the bed. Such a defect is extremely unpleasant and very noticeable externally, which aggravates the discomfort. Detachment is a disease, and it is called “onycholysis.” What do you need to know about it, and is it possible to get rid of the problem?
[1], [2], [3], [4], [5], [6]
What to do?
If skin growth under the nail is a symptom of a fungal disease, you need to prepare for complex treatment under the supervision of a qualified dermatologist. Doctors usually recommend:
The duration of treatment for nail fungus can be delayed for six months to a year or even more. The success of treatment largely depends on the scrupulous implementation of all the recommendations of the attending physician.
If the skin under the nail is in no way connected with a fungal infection, most likely we are talking about an overgrown hyponychium. In principle, this phenomenon is not at all dangerous and does not require any targeted correction. However, if the skin protrudes excessively above the fingertip, this causes some discomfort.
Manicurists recommend:
- Apply oil (for example, apricot) to the hyponychium area.
- Wait a minute or two.
- Gently move the peel with an orange stick.
- Be especially careful, as sudden movement may cause the hyponychium to come off.
- Repeat this procedure every time you perform a manicure.
Having discovered some strange formations on the skin or nails, it is better not to engage in self-diagnosis and not hope that the problem will go away on its own. It is worth consulting a dermatologist to rule out fungal diseases and other health problems.
Diseases of the nails, in which their shape and size change, always cause great discomfort in a person and significantly reduce his quality of life. Nails are a mirror that reflects the state of human health, and are often the first to indicate serious diseases of the body. Nail fungus accounts for half of all cases of disease. At different stages of the development of this disease, changes in the nails are expressed in one form or another and often have great similarities with a number of other diseases. Nails are often affected by lichen planus, psoriasis and eczema.
Causes of onycholysis
Doctors consider mechanical damage to the nail to be the most common cause of the disease. Detachment often occurs when there is a blow to the finger phalanx, when a hemorrhage forms under the nail, as well as when the nail plate is burned or “undermined” (accidentally or intentionally).
The next possible cause is an infectious skin disease - mainly of a fungal or microbial nature. In most patients, onycholysis develops after prolonged low-grade inflammation.
Allergies are a relatively rare cause. The development of nail disease due to allergies is associated with prolonged contact with an allergenic substance - for example, with a hyperreaction to latex or cleaning products.
Often the disease is a “continuation” of other dermatological and other problems - disorders of the endocrine system, neuroses, psoriasis or eczema, diseases of the vascular system.
There is information about the development of pathology against the background of prolonged or chaotic treatment with antibiotics.
Onycholysis after gel polish is also relatively common. The reasons for this phenomenon are still unknown, because the disease does not affect all representatives of the fair sex who use gel nail polish. Presumably, the problem may lie in the use of low-quality materials, as well as in improper correction and hypersensitivity of the girl’s body to the effects of chemical components and to the very process of drying the coating with ultraviolet light.
In a similar way, onycholysis can develop from shellac or from a means for removing it. Fortunately, this disease goes away on its own after stopping the use of provoking nail procedures.
Traumatic onycholysis
As the name implies, traumatic onycholysis develops under the influence of various types of trauma - both mechanical, chemical or physical damage.
Mechanical onycholysis can be a consequence of blows to the nail phalanx, bruises, compression, etc.
Chemical onycholysis is the result of exposure to various chemicals, detergents and cleaners, solvents, etc.
Physical onycholysis occurs under the influence of ultraviolet or other radiation, high or low temperatures.
[14], [15]
Nail hyponychia treatment: side effects, causes, list, stages
- 1 Fungus and aesthetic beauty
- 2 Provoking factors and causes of mycosis on the legs and arms
- 3 Symptoms of the disease
- 4 How is fungus diagnosed?
- 5 Treatment for mycosis of nails 5.1 Pharmaceuticals and their alternatives
- 5.2 Tablets to combat mycosis
- 5.3 Creams, sprays and ointments for nail fungus
- 5.4 Application of varnishes
- 5.5 Traditional recipes
- 5.6 Other treatments
Have you been trying to get rid of PARASITES for many years?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to get rid of parasites by taking every day...
Read more "
The most common ailment of the nail plate is mycosis of the toenails, caused by a fungus called red trichophyton. The nature and duration of treatment depends on the degree of damage.
Both children and adults get sick. But the older the patient, the more difficult it is for him to tolerate the symptoms and illness. The reason lies in the fact that with age the nail plate grows more slowly.
And the most important thing is precautions.
Fungus and aesthetic beauty
Onychomycosis can deprive many, and especially the fair sex, of a sense of beauty and confidence. After all, a feeling of discomfort is created that prevents you from enjoying a full life.
The fungus affects the nail plate, and the spores tend to expand near the skin of the nail plates, thereby causing active tissue destruction.
Many simply endure the infection for years without doing anything, and some of those infected are embarrassed to even see a doctor.
OUR READERS RECOMMEND!
Our readers successfully use Intoxic to get rid of parasites. Seeing how popular this product is, we decided to bring it to your attention. Read more here...
Provoking factors and causes of mycosis on the legs and arms
Failure to follow hygiene rules in beauty salons when working with undisinfected instruments leads to mycosis.
The causes of toenail fungus are caused by non-compliance with hygiene rules and an indifferent attitude towards health.
A trivial example is trying on and buying shoes in a store without disposable socks, or doing nail extensions in a beauty salon without first disinfecting the instruments. And after this, treatment for mycosis of the nails on the hands or feet, or even the feet, may be necessary.
Much attention should be paid to the condition of the shoes. Nail fungus occurs when a barefoot person visits public locker rooms, swimming pools, and showers. Allergies, weakened immunity, complications after illnesses provoke the disease.
Onychomycosis develops slowly, but has devastating consequences. Having destroyed the nail, it spreads throughout the skin, infecting more and more areas of the skin. Factors and causes of fungus:
- microcracks between the toes;
- dry skin on the legs and sweating;
- physiological narrowness in the interdigital area;
- flat feet;
- diseases of the cardiovascular and endocrine systems;
- stressful situations;
- metabolic disease;
- frostbite of the extremities;
- excessive exposure of nail plates to water.
Symptoms of the disease
The development of the fungus occurs under certain favorable conditions.
From the moment of infection to the first signs of mycosis, it takes from 1 to 7 days. Initially, with mycosis, peeling of the skin in the interdigital spaces is observed and an increasing itching occurs. Microcracks soon appear, and later the nail is damaged. Purulent discharge forms under the nails.
Cloudiness of unnatural shades appears on the nail plate. Onychomycosis begins to progress, with the nail becoming more massive and the nail becoming completely deformed. If treatment of nail mycosis is neglected, it destroys the nail plate, the nail peels off or falls off, and severe pain, itching and burning are felt.
Against this background, allergic reactions appear throughout the body.
How is fungus diagnosed?
To treat fungus, you need to get confirmation of the disease from a dermatologist. The specialist will prescribe a culture for mycosis, which involves scraping dead tissue from the nail plate. Analyzes will give a clear picture of the effect on the body.
If this is not associated with more serious diseases, then a treatment regimen for nail fungus from your doctor will not keep you waiting. The medicine is prescribed depending on the extent of the lesion and pathology. And the duration of treatment depends only on the degree of the disease. Self-medication is contraindicated, especially during pregnancy.
Since pregnant women need a special approach, the doctor will prescribe safe medications for mycosis without harm to the fetus.
Treatment for mycosis of nails
Treatment of toenail fungus at home will be successful only under the supervision and recommendations of a doctor.
Therapy begins immediately after the analysis is performed. Treatment of nail and foot fungus at home is effective if this is the initial stage. If the form is advanced, then comprehensive treatment for mycosis of the toenails is prescribed.
The recommendations of the attending physician must be followed strictly, otherwise it will take a long time to treat foot fungus. After all, the disappearance of the first signs of the disease does not indicate complete recovery.
The fungus can continue to affect the body for a long time and, under the first favorable conditions, begin to progress, so it is recommended to undergo a full course of drug treatment for foot fungus.
Pharmaceuticals and their alternatives
The most effective medications against fungus are:
- “Thermikon” (the drug is used for complicated lichen, no more than 1 week);
- "Mikoseptin";
- "Tsinkudan";
- "Undecin";
- "Travogen";
- "Nitrofungin".
If the fungus is pronounced, then the nail can be removed using Ureaplast, but fungicidal medications are additionally prescribed. An alternative to drug treatment is cosmetic products aimed at completely removing the affected nail.
This group includes: “Nogtivit” for fungus and “Nogtimycin”.
The ingredients (urea and stearic acid, tea tree essential oil, propylene glycol and triethanolamine) are aimed at getting rid of the diseased nail and have a beneficial effect on the growing new nail.
Tablets to combat mycosis
Nail mycosis tablets are taken along with other antifungal agents for effective treatment.
Tablets for fungal diseases - against onychomycosis - are toxic to the kidneys and liver, and the effectiveness is lower compared to ointments, creams, varnishes and drops. Therefore, the remedy for fungus in the form of tablets is taken in combination with other drugs.
They are often prescribed for diabetes mellitus, for patients over 50 years of age, and for severe immune problems.
The most common domestic and imported drugs for nail fungus: Lamisil, Fluconazole, Terbinafine, Itraconazole, Griseofulvin, Ketoconazole.
Creams, sprays and ointments for nail fungus
This group of anti-fungal drugs is intended for external use not only on affected skin areas, but also on healthy ones. The drugs have proven themselves quite well:
- Cream "Exoderil" (relieves itching, prevents recurrence of the disease, blocks the inflammatory process).
- Nizoral cream (a highly effective drug that can be used during pregnancy and lactation).
- Clotrimazole ointment (active and local action, without penetration into the bloodstream).
- Miconazole ointment (a strong drug that is prescribed after the ineffectiveness of other drugs; after applying the ointment, it is recommended to use a patch).
- Spray "Mycostop" (the ability to penetrate difficult areas of the skin and nails, used as a prophylactic drug when visiting swimming pools, gyms, saunas).
- Spray "Thermikon" (prevents and stops mycosis of the skin of the nails, but irregular use causes the condition to worsen).
Application of varnishes
Using nail polish for nail fungus is the most effective method of treating onychomycosis.
First of all, the use of varnish is aimed at destroying the source of infection and blocking its further spread under the nails. Therapeutic varnishes are produced on an oily or drying basis. Antifungal varnishes can be applied under decorative varnish; this does not result in their properties being lost. Therapeutic varnishes are transparent.
It is important to know the diagnosis correctly and complete the full course of treatment. If you choose the right varnish, the fungus dies within 48 hours. The proof of this is the reduction in symptoms. Healing varnishes can be purchased at the pharmacy.
The most common antifungal agents: Oflomelid, Lotseril, Oflomil, Batrafen, Belvedere, Demicten, Lamisil.
Folk recipes
At home, the disease can be easily eliminated using available means in the form of compresses and baths. Fungi “don’t like” an acidic environment, so lemon and vinegar are harmful to them; they need to be used to wipe the affected areas.
At the beginning of the disease, you can make a “mesh” with the help of iodine, the course of treatment is 3 weeks. Garlic is indispensable for home treatment. Garlic has healing properties in the form of juice, gruel and tincture. Used as a compress.
You can use freshly prepared coffee to make a foot bath for no more than 15 minutes throughout the week. Coffee not only has antibacterial properties, but also cleanses the skin of dead cells - a natural scrub.
Regardless of the stage of the disease, celandine fights the fungus using juice or tincture. Diet for nail fungus is important, you need to exclude sweets, eat more fresh vegetables and fruits.
Other treatments
When the condition of the nails is neglected, laser treatment is combined with medication.
To quickly get rid of nail and foot fungus in severe forms and when all means have not brought the desired result, laser therapy is prescribed. It is always effective, safe, convenient and painless.
The initial stages after the first procedure are already curable, but the course of treatment consists of 4 procedures with a break of a week. But severe forms of the disease require complex treatment, that is, the doctor additionally prescribes pills.
The procedure is not cheap, but there is always a guarantee of recovery, provided you follow the doctor’s recommendations.
Prevention
The consequences of nail fungus are disastrous. Therefore, it is better to use preventive measures and follow safety rules to avoid illness.
The main thing is to shower daily, wash your feet thoroughly between the toes, change socks daily, wear only comfortable shoes and your own, never put on wet shoes, use foot spray or shoe disinfection, make sure your nails are neat, avoid deformation, in public places, locker rooms, use replacement shoes. And at the first signs, see a doctor.
Source: https://lyambliya.parazit-zdor.ru/narodnye-sredstva/giponihij-nogtya-lechenie/
Risk factors
Considering all the possible causes of the disease, we can identify a number of factors that can lead to its development:
- injuries to fingers and nails, wearing uncomfortable shoes;
- various dermatological diseases;
- systemic diseases (pathologies of blood vessels, central nervous system, digestive tract);
- endocrine pathologies;
- infections (microbial, fungal);
- contact with chemicals, radiation.
[16], [17], [18], [19], [20], [21], [22], [23]
Pathogenesis
Pathogenetic characteristic factors of this disease can be all kinds of injuries and other disorders of the structure of the distal segment of the nail plate. Pathology in some cases may have professional characteristics - for example, detachment often occurs in laundresses, dishwashers, etc.
Acute and chronic poisoning, local intoxication effects, neurotrophic problems, skin diseases, and infections are also important.
Detachment of the plate from the nail bed in most cases begins on the free side, but in some cases there is lateral separation. Most often, the detachment is partial: a cavity is formed under the plate, which separates the nail from the soft tissues of the digital phalanx.
Symptoms of onycholysis
The main characteristic symptom of the disease is detachment of the nail plate, which often begins on the free side and worsens as it approaches the nail base. In most cases, the detachment is not complete and occupies no more than ½ of the entire surface of the plate. The formed cavity has a light gray tint: the nail does not change, its surface remains smooth. If the disease is caused by fungi or bacteria, then the nail may change shape, and the surface becomes lumpy and uneven.
The first signs of the disease may be as follows:
- a void forms under the nail;
- the border of the deserted zone is uneven;
- the color of the plate may change in color: for example, after an injury, the nail may become purple or bluish;
- the skin located under the nail, sometimes thickens;
- the shape of the nail plate may remain the same or change.
Nail damage: elimination, treatment
Nail plate. It is a tissue derivative arising from three zones of the nail bed. Fully grows in length in 70-160 days.
Nail bed. Consists of three parts: the dorsum, the germinative matrix (also known as the ventral floor), and the sterile matrix (also known as the ventral nail bed). The proximal end of the nail plate originates between the dorsum and the U-shaped germinal matrix of the nail bed.
Nail fold (eponychial fold). The proximal part of the nail plate is located under the nail fold. The skin on the back of the nail fold is the nail fold (it is located on top of the back covering of the nail bed). The thin plate extending from the nail fold to the back of the nail plate is called the eponychium. The lunula is a curved, opaque stripe on the nail distal to the eponychium at the junction of the germinal and sterile matrix.
Hyponychia. This is an accumulation of keratin between the distal part of the nail plate and the nail bed. Thanks to its strong fusion, it is resistant to infection.
Onycholysis during pregnancy
Detachment of the nail plates often occurs in pregnant women. This can be explained by many reasons:
- intense hormonal changes in the body;
- decreased immunity;
- deficiency of certain vitamins and minerals;
- swelling and weight gain, which creates additional stress on the lower limbs.
To eliminate onycholysis, pregnant women are recommended to limit themselves to local treatment, without resorting to oral administration of drugs. Systemic medications can have a negative impact on the development of the fetus and also pose a threat to the further normal course of pregnancy.
It is preferable to take vitamin complexes created specifically for pregnant women, as well as carry out external treatment with ointments or folk remedies.
Onycholysis in a child
The disease can occur in patients of any age, and children are no exception. In a child, onycholysis may indicate a disorder of systemic functions - for example, disorders of the digestive system, endocrine system. Often, poor nutrition or a deficiency of vitamins in the diet is to blame.
Detachment often occurs in children who have the habit of biting their nails. Also, the impetus for the development of pathology can be strong experiences, conflicts, and depressive states.
However, the most common cause of detachment is fungal infection. A child can become infected with a fungal infection in the pool, sports locker room or on the beach.
Since there can be many causes of the disease, it is necessary to accurately identify the exact cause from a doctor. He will prescribe the correct treatment.
The appearance of detachment of the nail plates in a child cannot be ignored: this may indicate serious disturbances in the functioning of the internal organs.
Hyponychium grows under the nail - All about the fungus
Have you been trying to cure FUNGUS for many years?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure fungus by taking the product for 147 rubles every day...
Read more "
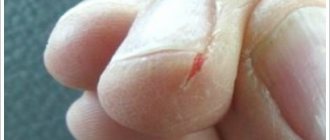
Big toes are prone to injury. Often people encounter cuts, abrasions, bruises, and splinters. Children are most vulnerable because their skin is more delicate than that of adults. If the affected area is not treated with antiseptic agents in time, inflammation may begin. The skin turns red and pus appears under the nail on the big toe.
In medicine, this condition is called panaritium. It is characterized by inflammation of the soft tissues of the finger, redness and swelling, severe pain, the appearance of pus, and the inability to move the phalanges of the finger. Perhaps an increase in temperature and the appearance of severe throbbing pain.
OUR READERS RECOMMEND!
Our readers successfully use Tinedol to treat nail fungus. Seeing how popular this product is, we decided to bring it to your attention. Read more here...
The disease develops when bacteria or other infections enter the microtrauma. Panaritium is caused by streptococci, staphylococci or fungi. A mixed type of disease is possible.
Causes of the disease
Inflammation can affect any finger or toe. But the big toes are more vulnerable. They are more likely to be injured and suffer more than others from tight shoes. They are also much more likely to be treated incorrectly during a pedicure.
The main causes of felon include the following:
- any injuries, bruises, cuts that were not treated with antiseptics immediately after receiving them. Often the cause is an ordinary splinter;
- the appearance of purulent fluid causes an ingrown toenail;
- poor personal hygiene
- nail or foot fungus (also known as onochemical fungus);
- diabetes;
- disturbance of blood flow in the lower extremities.
The disease is common in children. It affects those babies who pick hangnails or bite and suck their nails (little children often suck their big toes); it occurs in infants when their nails are cut carelessly.
The pathology appears in people whose work is related to wood and is dangerous: joiners, carpenters, agricultural workers.
Types of disease
Paranicia can occur in two forms:
- acute form - this type is observed if the disease develops rapidly. The skin swells and turns red, severe pain is felt, the finger becomes immobilized, and pus comes out from under the toenail. In these cases, you should immediately consult a doctor;
- chronic form - in these cases discomfort is felt. In the normal state there is no pain, but when pressing on the nail, a person feels painful sensations. The finger swells a little, and slight redness is noticeable. This type of panaritium is treated with conservative and folk methods.
How to treat the disease
If you find pus under your nail, it is recommended that you make an appointment with your doctor. He will assess your general condition and help you choose treatment. If the disease is in the early stages of development, then it will be enough to use antiseptic ointments and take a course of antibiotics. In cases where the disease is advanced, surgeons resort to surgery.
Doctors prescribe the following as medicinal ointments:
- antibacterial ointment "Levomekol";
- Dioxidine ointment;
- Vishnevsky ointment.
Night applications are made on their basis. To do this, take a bandage, fold it several times and soak it with the necessary ointment. After this, the application is applied to the affected surface and fixed with a plaster or bandage.
Doctors prescribe treatment based on what caused the inflammation. If the causative agents are streptococci or staphylococci, then a course of antibiotics is indispensable. It is prohibited to take these medications on your own, only after the recommendation of a doctor. The dosage and duration of administration should be strictly observed. As a rule, Amoxiclav is prescribed.
If the infection is caused by fungi, then antifungal drugs are prescribed. These can be ointments: “Ichthyol” or “Tetracycline”. Or a course of drugs to be taken orally. The most common: Fluconazole solution, Nystatin.
To relieve pain, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed: Ibuprofen, Paracetamol.
If traditional therapy does not help, then doctors resort to opening the abscess. The operation is performed under local anesthesia, the affected finger is treated with iodonate. When the abscess is at the free edge, the plate is cut off with scissors and an incision is made.
When pus accumulates under the nail, it is necessary to completely remove the entire nail plate. The wound is treated with medications, and a drain is inserted into it to avoid tightening. In a few days the doctor will remove it.
The first five to seven days of dressing will be carried out under the supervision of a doctor, then you will need to independently treat the affected area until complete recovery.
Treatment with folk remedies
Traditional methods of treating purulent inflammation can be used as additional means to the main therapy. You can use any prescription only after consulting your doctor.
Hot baths with soda and salt help relieve inflammation, draw out pus and reduce pain. The solution must be concentrated. Dissolve five tablespoons of salt and one tablespoon of soda in a liter of hot water. The water temperature should be 50 - 60 degrees. Place the affected finger in the bath and hold for fifteen minutes.
For salt baths, only hot water is used, it should be done at a temperature that you can tolerate. Hot water wrinkles the skin, pushing pus out from under the nail, and a salty solution helps draw out purulent fluid.
- Compresses will help draw out the pus. As an active ingredient, you can take garlic (it should be put through a press), raw beets, crushed aloe or plantain leaves. Compresses are applied overnight to ensure long-term contact of the treatment with the abscess and secured with a sterile bandage.
- A weak solution of potassium permanganate will help relieve inflammation (focus on the pale pink color). Prepare a warm bath by adding a little manganese. Keep your sore foot in it for 7 – 8 minutes. These procedures are recommended to be carried out every day until the patient's condition improves.
- Baths with the addition of medicinal herbs have antiseptic properties. Chamomile, string, and calendula will help with this. Use only warm water, as hot water can increase the area of suppuration.
- Take chamomile and sage in equal parts, add St. John's wort, lilac and plantain leaves to them (take them in the same proportions). Pour in a liter of water and simmer over low heat for five minutes. After cooking, add a teaspoon of baking soda. Cool the broth to a pleasant, warm temperature and take the bath for fifteen minutes.
After taking the bath, treat the abscess with an antiseptic, carefully lift the nail plate and alternately press on the fingertip and the nail itself until all the contents come out of the purulent pocket.
Take propolis tincture. Add warm water to it at the rate of one part tincture to five parts liquid. Immerse your finger three to four times a day, hold for at least fifteen minutes. After a few days, the purulent contents will come out and healing of the sore finger will begin. It is important! Clean your finger with alcohol after removing the pus.
Take castor oil and heat it in a water bath. Soak a cotton swab or piece of bandage in it. Apply to the sore nail, secure with a band-aid, remove after two to three hours.
Vishnevsky ointment and fir oil will help in the treatment of felon. Mix three parts ointment and seven parts fir oil. Apply the compress to the sore finger, secure on top with plastic wrap and adhesive tape. Wear it for six to seven hours, then take it off. This remedy accelerates the process of maturation of the abscess.
Conclusions
Panaritium is a painful condition in which the skin under and around the nails becomes inflamed. It turns red, swells, and pus appears under the toenail. When the first symptoms appear, you should consult a doctor.
Along with conservative therapy, home treatment methods can be used. In advanced cases, surgical intervention is possible, during which the abscess is opened and the nail plate is completely removed.
Complications and consequences
Onycholysis certainly does not pose any danger to the patient's life. The disease can even go away on its own, provided that the provoking factor is eliminated. However, if the detachment is caused by exposure to an infectious pathogen, then if left untreated, the infection can spread and gradually capture all the nails, both on the upper and lower extremities.
Nails that are affected by infection eventually become unattractive, brittle, and discolored, which affects the quality of daily life.
If the disease is accompanied by a fungal infection, then it can spread, in addition to the nails, also to the skin of the feet and/or palms.
[41], [42], [43], [44], [45], [46], [47], [48]
Diagnosis of onycholysis
To diagnose and treat the disease, you need to consult a dermatologist. If a dermatologist discovers specific causes for the development of the disease, he may refer the patient for further examination to an endocrinologist, gastroenterologist, or allergist.
In order not to make a mistake with the choice of treatment, it is very important for the doctor to correctly determine the cause of the disease. To do this, he will first carefully examine the affected nails and interview the patient about his complaints and symptoms.
Tests are prescribed to identify the causative agent of the infection - for example, to determine the presence of fungus, streptococcus or staphylococcus. In addition, a general blood test may be prescribed to assess the functioning of the whole body, as well as to identify the inflammatory process.
Instrumental diagnostics for nail pathologies are rarely used, which may depend on the expected cause of the detachment.
[49], [50], [51], [52]
Why does skin grow under the nail?
Various nail disorders require close attention and adequate timely correction. After all, sometimes alarming symptoms indicate the development of diseases.
Skin grows
The appearance of skin under the nails is actually a fairly common symptom, although not all cosmetologists and dermatologists are aware of its features. This phenomenon can be caused by various factors:
- Various growths and formations under the nails are often found when affected by fungal diseases. Such growths may not cause any discomfort, but greatly worsen the appearance. And as the pathology progresses, detachment and destruction of the nail plate may occur. You can suspect the occurrence of fungal infections by itching, destruction and thickening of the nail, as well as a change in its color. Similar ailments are often manifested by excessive peeling of the epidermis (near the nail). Much more often, fungal diseases affect the toenails.
- Sometimes the skin under the nail is nothing more than an overgrown hyponychium. This term is used to refer to the growth layer of the epidermis, which forms the subungual bed. Normally, the hyponychium lasts until the area where the nail plate separates from the bed and passes into the free edge. However, in some cases, such a layer grows further and is attached to the nail from the inside (by several millimeters). If its integrity is violated (for example, during a manicure), you may experience bleeding. An overgrown hyponychium can cause discomfort and even pain. And manicure experts say that this problem is most often observed in girls who extend their nails to excessive length. The exact reasons for the occurrence of such a disorder are unknown; perhaps it is an individual characteristic of the body, or perhaps its protective function.
To determine why the skin under the nail is growing, you need to consult a cosmetologist and dermatologist. The doctor will send the patient to the laboratory where, using a simple test, it will be possible to confirm or deny the presence of a fungal disease.
What to do?
If skin growth under the nail is a symptom of a fungal disease, you need to prepare for complex treatment under the supervision of a qualified dermatologist. Doctors usually recommend:
- Take systemic antifungal medications.
- Treat affected areas of nails and surrounding skin with various antifungal medications.
- Take medications that improve blood circulation in the periphery.
- Use products that strengthen the immune system.
The duration of treatment for nail fungus can be delayed for six months to a year or even more. The success of treatment largely depends on the scrupulous implementation of all the recommendations of the attending physician.
If the skin under the nail is in no way connected with a fungal infection, most likely we are talking about an overgrown hyponychium. In principle, this phenomenon is not at all dangerous and does not require any targeted correction. However, if the skin protrudes excessively above the fingertip, this causes some discomfort.
Manicurists recommend:
- Apply oil (for example, apricot) to the hyponychium area.
- Wait a minute or two.
- Gently move the peel with an orange stick.
- Be especially careful, as sudden movement may cause the hyponychium to come off.
- Repeat this procedure every time you perform a manicure.
Having discovered some strange formations on the skin or nails, it is better not to engage in self-diagnosis and not hope that the problem will go away on its own. It is worth consulting a dermatologist to rule out fungal diseases and other health problems.
Differential diagnosis
Differential diagnosis is most often carried out with other dystrophic processes of the nails:
- hapalonychia – softening of the nails;
- brittle nails due to vitamin deficiency;
- onychomadesis – complete detachment of the nail;
- onychorrhexis - longitudinal splitting of the nail;
- onychoschisis - transverse splitting of the nail;
- trachnonychia - roughness and peeling of the plate;
- nail patterns - wear on the free side of the plate.
In addition, the disease should be distinguished from mycoses, Bowen's disease, lichen planus, and nail psoriasis.
The differences between onycholysis and fungus are significant, although in some cases the differentiation of diseases can be difficult:
- nail fungus is transmitted from person to person, and non-infectious onycholysis is not contagious;
- nail detachment, as a rule, is not accompanied by a significant change in the color and shape of the plate: the fungus makes the nail rough and radically changes its color;
- with fungus, patients complain of a feeling of itching and irritation, but with normal detachment there are no such symptoms;
- with fungus, the smell of the feet changes;
- fungus will never appear as a result of injury.
Diagnosis can present some difficulties if a person has onychomycosis and onycholysis at the same time - such situations, by the way, happen often. In this case, laboratory tests will be required.
How to treat hyponychia
A nail is a hard, horny, plastic formation on the skin of the tips of the toes and hands. Nail growth occurs from a bursa-like depression of the epidermis located on the back of the toes and hands.
The formation of a nail occurs in its matrix (root), which is a special tissue that occupies the lower part of its bursa.
The matrix area is adjacent to the nail bed, located distal to the body, with which the lower surface of the nail plate is firmly combined from the longitudinal ridges to the hyponychium.
The hyponychium is the dorsal portion of the epidermis between the nail bed and the tip of the finger or toe. The nail fold is the area of the skin fold that covers the nail laterally and proximally.
The epithelial skin that is loosely adjacent to the nail is called the cuticle.
In its natural state, the nail has a soft pink color, except for the crescent area, which is white.
The reason for the light color of the socket is the more intense activity of cell division in this area, a weaker supply of capillaries and the formation of intracellular keratohyalin.
Depending on a person’s individual characteristics and age, the thickness and size of nails can vary significantly.
Histologically, the differentiation products of the nail matrix differ. The upper layer is more layered, dense and flat, significantly elongated along the cell, and the inner layer is a large accumulation of cubic cells, which differ in electron-optical and histochemical parameters.
Favorable mechanical properties of the nail are ensured by its layered structure with an elastic lower section and a hard upper section. On the lower side, the free part of the nail is adjacent to the third layer, which is a differentiation product of the hyponychium. In the presence of pathological processes, it can grow greatly.
The rate of nail growth depends on the rate of formation of new cells in the matrix. The cells of the matrix, in contrast to the mechanism of keratinization of the epidermis, are transformed without the keratohyaline stage and are lamellar horny structures, the cells of which contain remnants of the nucleus.
Throughout a person's life, fingernails and toenails grow continuously unless prevented by traumatic or painful influences. However, with age, the growth rate decreases.
The approximate growth rate of toenails is 1 mm per month, and the nail plate grows completely in about 1-1.5 years. Moreover, the nails of different toes grow at different rates. The slowest speed is on the big toes.
Fingernails grow several times faster. Children and young women's nails grow faster than young men's, but after age 40 this ratio changes. During daylight hours, nail growth is faster than during dark hours.
Nail growth increases due to injury, pregnancy, and after surgical removal of the nail. But poor nutrition and various common diseases, on the contrary, slow down the growth of nails.
Symptoms of nail diseases
Human nails suffer from various diseases. Here are the symptoms of the most common ones:
- Onycholysis – detachment of the nail plate from the nail bed;
- Leukonychia is a disease in which the nail turns white;
- Pachyonychia - thickening of the nail plate;
- Hapalonychia is a disease in which the nail plate becomes too thin;
- Onychorrhexis - longitudinal splitting of the nail plate;
- Onychogryphosis is a change in the thickness and color of the nail plate when it bends into a beak;
- Nail bed hyperkeratosis is a thickening of the nail bed that often occurs in response to fungal diseases;
- Koilonychia – change in the shape of the nail plate in the form of a spoon;
- Onychoschisis - transverse splitting of the nail plate;
- Onychomycosis – nail fungus;
- Onychomadesis – complete loss of the nail plate;
- Onychocryptosis - ingrown nail.
Of all the above diseases, onychomycosis (nail fungus) and onychocryptosis (ingrown toenail) are the most common.
Onychomycosis is a very tenacious infectious disease that can survive even on fallen nail plates for several months. You can catch it through contaminated shoes and in public places - saunas and baths, gyms and swimming pools.
Nail fungus begins, usually on the skin and in the interdigital folds, and is accompanied by severe itching and burning, and peeling of the skin. If treatment for nail fungus is not started immediately, it will develop into a more severe form; cracks, ulcers, and blisters may appear on the skin. And only after this the disease spreads to the toenails.
Externally, the color of the nail changes, it becomes opaque, then begins to deteriorate and crumble. If nail fungus is not treated, it will spread throughout the entire nail and spread to the inside of the nail. Therefore, it will be difficult to overcome even after removing the nail.
As a rule, treatment of nail fungus is medicinal, using special ointments and tablets.
Ingrown nail (onychocryptosis) is a disease caused by the ingrowth of the nail plate into the side of the nail fold. More often this happens on one side. The disease is accompanied by pain, redness and swelling of the nail fold. As the disease progresses, hypergranulation and purulent discharge can be observed.
Most often, the disease occurs on the feet, but it happens that it also appears on the fingernails. Most often, this disease can be seen in pregnant women and people of puberty.
The causes of the disease are various factors. These include heredity and nail deformations, improper pedicure or hormonal changes in the body, and the consequences of fungal diseases.
Treatment of onycholysis
The treatment regimen for the disease depends on its cause. But, in any case, an integrated approach is used - and this especially applies to progressive and sluggish pathologies.
How to quickly cure onycholysis? The doctor can give some advice on this matter. For example, he will advise limiting contact with chemicals, detergents and cleaning products, and also using protective finger caps or gloves. In addition to appropriate careful nail care, the doctor will prescribe medications for local and systemic action.
Structure of a natural nail • EstPortal
Natural nails can already be considered a rarity, because most people regularly extend them, cover them with gel polish, do bio-reinforcement or perform other manipulations. And in order for all these actions to be performed correctly, the manicurist must know the anatomy of the nail. After all, the nail performs an important protective function, and is not only a field for design.
Nails are horny plates on the back surface of the ends of the fingers. The nail has a free edge, and the other three sides are limited by ridges: posterior and lateral lateral. The thickness of the nail is less than 0.5 mm, but usually not less than 0.3 mm.
Anatomical structure of the nail:
- nail plate;
- posterior nail fold;
- lateral nail folds;
- nail root;
- nail frenulum;
- bony phalanx;
- matrix;
- hyponychia;
- eponychium.
The nail folds surround the nail and form the nail sinuses at the junction with the nail plate. When doing nail extensions, the technician needs to pay special attention to these areas, since it is there that acrylates (esters of acrylic acid or its salts) begin to come off most quickly.
The root of the nail is located under the posterior ridge.
The nail socket is the visible part of the nail root that protrudes from under the nail fold as a whitish, crescent-shaped area.
The eponychium is the living skin at the base of the nail plate. Although most people mistakenly consider it a cuticle. As the nail plate grows, it detaches the lower layer of skin from under the eponychium and, as it were, drags it along with it. Dead tissue moves to the surface of the growing nail from under the roll of living skin. This thin layer of skin is the cuticle. The eponychium serves as protection for the nail root and its growth zone. It is formed due to the germ layer of the epidermis. The back ridge partially dries out and becomes part of the nail plate and grows slightly over the nail.
The part of the cuticle that grows along the length of the nail, sometimes occupying almost half of it, is called pterygium. It interferes with the application of coating to the nails and gives them an unesthetic appearance. Therefore, it must be removed with a milling cutter or cut off with a special tool.
The nail plate is the result of matrix cell division. This is the germ part of the nail, which is closely connected to the root. The matrix and the nail root do not have a clear transition boundary. At the same time, the matrix belongs to the germ layer of the epithelium, and the nail itself constitutes the stratum corneum.
The matrix originates from the nail bed - hyponychium. Onychoblasts are matrix cells that continuously and very quickly divide and turn into horny plates of the nail, lengthening and thickening it. The matrix cells are very well equipped with blood vessels and nerve endings. It is the condition of the matrix that determines the quality of the nail plate, its thickness, length, growth rate and structure. If anything happens to the matrix, it is immediately reflected on the nail plate.
The bridle of the nail performs a fixing function. She keeps the nail in place. The frenulum is formed thanks to the collagen fibers of the hyponychium, which are located towards the phalanx and connect there with the periosteum. The hyponychium reaches the free edge of the nail, turning into a fold of skin under the edge of the nail.
Chemical composition of natural nail and its physiology
The basis of the nail plate is keratin - a protein. Keratin is a complex protein and at the same time one of the strongest proteins in living nature, which contains sulfur. The chemical composition of the nail includes calcium, phosphorus, zinc and, not surprisingly, arsenic. Another interesting thing is that nails contain a fat-like substance - cholesterol.
The physical and chemical aspects of the functioning of the nail are directly related to the work of the manicurist. For example, you need to know that nails absorb water well. They absorb various oils and fats even better, even better than skin does. On the one hand, this is useful to know when treating and restoring a nail, and on the other hand, it directly affects the adhesion of the nail plate to coatings.
Nails are completely dependent on the skin. If it is oily, then your nails may suffer from the same problem; if it is too dry, the same applies. Being in a warm and humid environment, they increase in size. Cold and dryness cause the nail plate to shrink in size.
Such properties must be taken into account when choosing a composition for coating the nail. The nail changes its characteristics and even its size, which means the coating should be moderately elastic, but at the same time remain dense. Modern coatings are approximately 20 times stronger than the nail plate.
Many people are concerned about the appearance of transverse grooves or white granular spots (leukonychia) on the nail plate. All this is connected with the matrix and especially the impact on it, its traumatic nature. The spots indicate that the process of keratinization of cells has been disrupted. This may be due to metabolic disorders. If there are a lot of such spots on the nails, it would be a good idea to seek advice from a dermatologist and therapist, and then, if necessary, to more specialized specialists.
The growth patterns of the nail plate are as follows: it will completely change only after 3-4 months. Therefore, when restoring and treating a nail, you cannot expect quick results. It’s a shame, but men’s nails grow faster than women’s. During the cold season, the growth process slows down.
Interaction of the nail with artificial coating
The nail itself is a fairly strong structure capable of self-healing. Many people are interested in the question: “Will it harm your own nails when coated with different products? What is the threat and is it worth worrying about?”
The most vulnerable structure of the nail is the matrix. It is its damage that should be feared in the first place, because this can lead to a deterioration in the condition of the entire nail. The matrix is a rather capricious thing that reacts to any changes in the body (increase in temperature, vibration, blood circulation) and in the environment. The nutrients and oxygen that blood flow brings are very important for the matrix.
Division is the main function of the matrix. At the same time, after division, the mother cell prepares for the next one, and the new cell is gradually saturated with keratin and pushes its predecessors forward so that they form the nail plate, due to this the nail grows. Matrix cells form the nail socket. As they exist, the matrix cells that move forward contain more and more keratin.
The life of nails is not easy; they take on both chemical and mechanical influences. The free edge of the nail is especially susceptible to various impacts. The nail plate is constantly forced to withstand the external environment. Many people think that nail covering only brings additional stress to the nails, “nails don’t breathe” and so on.
An acrylic or gel coating eliminates the need for the nail to withstand environmental factors, that is, it protects the nail from external influences. At the same time, the horn cells that form the nail do not need direct contact with air (“breathing”), because the entire structure of the nail receives oxygen and other nutrients solely through blood circulation. Whether there is a coating on the nails or whether they are natural does not matter if there are disturbances in the local blood circulation and the condition of the skin of the hands. But in the first case, at least scratches, detergents and other negative influences will destroy the varnish, gel or acrylic, and not the nail itself.
Masters and clients note that the nail plate becomes stronger and smoother, and nails grow faster with regular gel manicures. Of course, there is also a reverse trend. But it is typical only if the procedure for removing the gel is violated or the nail plate is damaged by the master. For example, when during a hardware manicure a cutter is used to cut off not only the gel, but also the layer of the nail plate. Or when they do a manicure “under the cuticle,” exceeding the permissible load on the nail root and thereby damaging the matrix.
A natural nail is a full-fledged biological structure that has its own laws of functioning and regulates itself. This does not mean that any interference is harmful, but it does mean that it can become so if you do not know how the system works. Therefore, the main principle, as in any area of personal care, is beauty = health.
Anna BUNYAK
Download NULLed WordPress ThemesDownload NULLed WordPress ThemesPremium WordPress Themes DownloadPremium WordPress Themes Downloaddownload udemy paid course for free
Prevention
Preventive measures are as follows:
- in order to avoid nail detachment, it is necessary to observe safety measures when carrying out manicure and pedicure procedures;
- if coating or liquid nail preparations are used, you should take care of their quality in advance;
- when using chemical detergents or cleaning agents, it is important to use additional protective gloves or finger caps;
- it is important to eat properly and nutritiously to avoid vitamin deficiency and weakened immunity;
- in winter and spring, you can additionally take vitamin complex preparations;
- It is necessary to promptly and efficiently treat any infectious diseases, as well as systemic pathologies of a chronic nature.
[54], [55], [56], [57], [58]
Forecast
The disease has a relatively favorable prognosis. Non-infectious pathology can stop on its own, provided that the root cause is eliminated. Infectious onycholysis requires adequate treatment: otherwise the situation may be aggravated by the formation of additional inflammatory foci, partial destruction and deformation of the nail.
Onycholysis is a complex and long-lasting disease, so you need to be patient and treat it correctly, taking into account the cause of its occurrence.
[59], [60], [61]
Source